An organ in the respiratory system – The lungs, a vital organ in the respiratory system, play a crucial role in the exchange of gases, ensuring the body’s oxygen supply and removal of carbon dioxide. Their intricate structure and function make them essential for maintaining life.
The lungs, a vital organ in the respiratory system, enable us to breathe and exchange gases. Like the intricate network of payment systems explored in an introduction to payment systems martin goodman , the lungs facilitate a seamless flow of oxygen and carbon dioxide, ensuring the smooth functioning of our bodies.
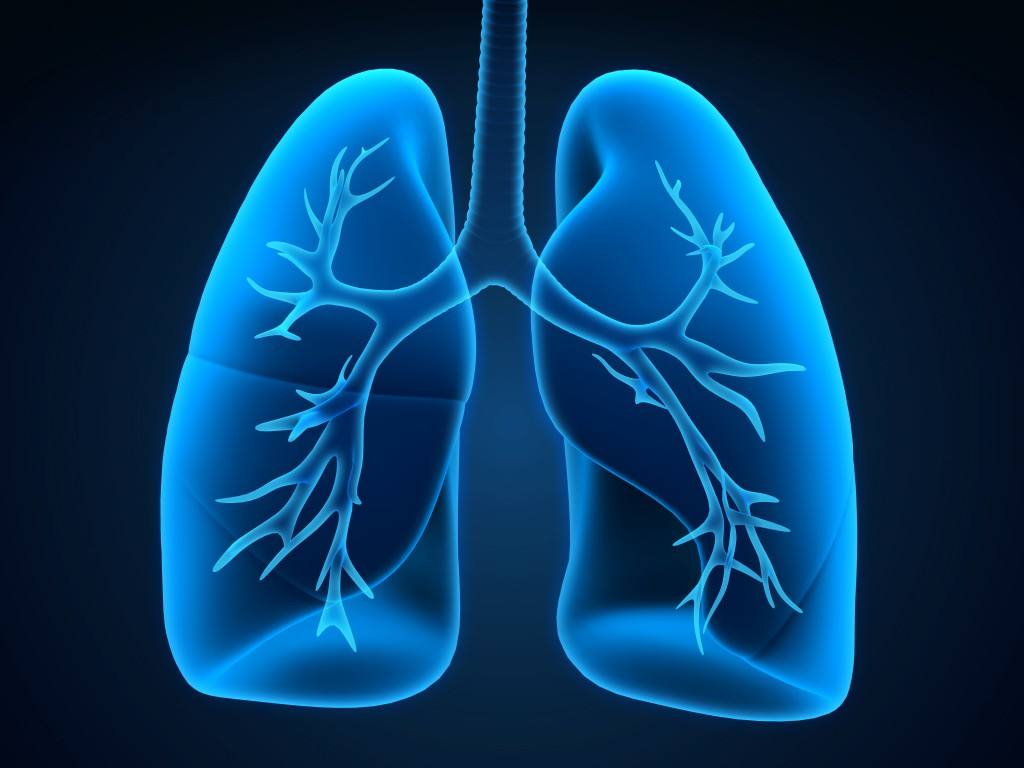
Located in the thoracic cavity, the lungs are composed of spongy tissue divided into lobes and covered by a thin membrane called the pleura. The internal structure consists of bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli, which provide a vast surface area for gas exchange.
Just like an organ in the respiratory system helps us breathe, an improved sewer system would solve these flood drainage problems. The lungs, for example, allow us to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. Similarly, a well-maintained sewer system can efficiently drain excess water, preventing flooding and its associated hazards.
Investing in infrastructure upgrades, such as an improved sewer system , is crucial for creating resilient communities and ensuring the well-being of our respiratory systems.
Structure and Anatomy of the Lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system, responsible for gas exchange between the body and the external environment. They are located in the thoracic cavity, protected by the rib cage. The lungs are paired organs, with the right lung being slightly larger than the left.
Each lung is divided into lobes: the right lung has three lobes (upper, middle, and lower), while the left lung has two lobes (upper and lower).
Lungs, a vital organ in our respiratory system, play a crucial role in gas exchange. Just like an intrusion detection system cannot prevent DoS attacks an intrusion detection system cannot prevent dos attacks , our lungs can sometimes be vulnerable to external threats.
However, they have remarkable resilience and can often repair themselves, much like our bodies’ natural defenses against malicious online attacks.
The lungs have a spongy texture and are composed of millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli. The alveoli are lined with capillaries, which are tiny blood vessels that allow for the exchange of gases between the air and the bloodstream.
The lungs are also covered by a thin layer of pleura, a membrane that helps to lubricate the lungs and reduce friction during breathing.
The lungs, a vital organ in the respiratory system, allow us to breathe and function. Just like our computers need an operating system to run, so do our lungs require a healthy environment. Similar to how an example of an open source operating system can improve a computer’s performance, maintaining clean air and avoiding pollutants can enhance the lungs’ ability to provide oxygen to our bodies.
Histologically, the lungs are composed of a variety of cell types, including:
- Alveolar cells:These cells line the alveoli and facilitate gas exchange.
- Bronchial cells:These cells line the bronchi, the airways that carry air to and from the lungs.
- Ciliated cells:These cells line the airways and help to clear mucus and debris from the lungs.
- Goblet cells:These cells secrete mucus, which helps to keep the airways moist.
Function and Physiology of the Lungs
The primary function of the lungs is to facilitate gas exchange between the body and the external environment. This process involves the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Oxygen is essential for cellular respiration, while carbon dioxide is a waste product of cellular metabolism.
The lungs facilitate gas exchange through the following mechanisms:
- Ventilation:This refers to the movement of air into and out of the lungs. Ventilation is driven by the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles.
- Diffusion:This refers to the movement of gases across a concentration gradient. Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the bloodstream into the alveoli.
- Perfusion:This refers to the flow of blood through the lungs. Perfusion is essential for gas exchange, as it brings oxygen-poor blood to the lungs and removes oxygen-rich blood from the lungs.
The lungs also play a role in maintaining respiratory homeostasis. They help to regulate blood pH by removing carbon dioxide, which can cause acidosis if it accumulates in the body. The lungs also help to regulate body temperature by releasing heat when the body is too warm and conserving heat when the body is too cold.
Let’s talk about your lungs, the vital organs that help you breathe. Just like how an introduction to information systems can help you understand the basics of IT, your lungs are essential for understanding the fundamentals of life itself. They allow you to take in oxygen, which is the fuel that powers your body and keeps you going.
Innervation and Blood Supply of the Lungs
The lungs are innervated by the vagus nerve, which controls the muscles of the airways and the blood vessels of the lungs. The vagus nerve also helps to regulate the rate and depth of breathing.
Lungs, the oxygen-pumping organs in our bodies, share a fascinating connection with icy small solar system bodies . These celestial wanderers, like frozen comets, often contain complex organic molecules that hint at the potential for life beyond Earth. Just as our lungs breathe life into our bodies, these icy visitors may hold clues to the origins of life in our solar system and beyond.
The lungs are supplied with blood by the pulmonary arteries, which carry oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs. The pulmonary arteries branch into smaller and smaller vessels, eventually forming capillaries that surround the alveoli. The capillaries allow for the exchange of gases between the air and the bloodstream.
The lungs, essential organs in the respiratory system, allow us to breathe and take in oxygen. Just like our lungs, businesses need a clear understanding of their systems and processes to function effectively. Check out an introduction to business systems analysis to learn how businesses can optimize their systems for maximum performance, just like our lungs do for our bodies.
The oxygen-rich blood then flows back to the heart via the pulmonary veins.
The lungs have a unique dual blood supply. In addition to the pulmonary circulation, the lungs also receive blood from the bronchial circulation. The bronchial circulation supplies oxygen and nutrients to the tissues of the lungs themselves.
The lungs, like an executive support system , facilitate efficient breathing by managing the flow of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Their intricate structure, akin to a well-oiled team, ensures seamless gas exchange, mirroring the smooth operations of an executive support system that empowers leaders to excel.
Clinical Significance of the Lungs: An Organ In The Respiratory System
The lungs are susceptible to a variety of diseases and disorders, including:
- Pneumonia:This is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
- Bronchitis:This is an inflammation of the bronchi, the airways that carry air to and from the lungs.
- Emphysema:This is a chronic lung disease that causes damage to the alveoli, leading to shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
- Lung cancer:This is a cancer that starts in the lungs.
The symptoms of lung disease can vary depending on the specific condition. However, some common symptoms include:
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
The diagnosis of lung disease typically involves a physical examination, a chest X-ray, and a pulmonary function test. Treatment for lung disease depends on the specific condition and may include antibiotics, bronchodilators, steroids, and surgery.
Closing Notes
The lungs’ ability to facilitate respiration is essential for maintaining homeostasis and supporting the body’s metabolic processes. Understanding their structure, function, and clinical significance is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the respiratory system and its impact on overall health.
The lungs, a vital organ in our respiratory system, are like an operating system that consists of a single large program , coordinating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Just as this program manages the computer’s hardware, the lungs work tirelessly to ensure our bodies have the breath of life.
Common Queries
What is the primary function of the lungs?
The primary function of the lungs is to facilitate gas exchange, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled.
What are the common diseases associated with the lungs?
Common lung diseases include asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, and lung cancer.
How can I maintain healthy lungs?
Maintaining healthy lungs involves avoiding smoking, engaging in regular exercise, and getting vaccinated against respiratory infections.