An organism with tracheal system – Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of organisms with tracheal systems! These creatures possess a unique respiratory system that allows them to breathe efficiently in diverse environments. From insects to arachnids, the tracheal system is a marvel of evolution, and we’re here to unravel its secrets.
An organism with a tracheal system, like an insect, has a network of tubes that deliver oxygen directly to its cells. Just like an operating system assigns memory to programs , the tracheal system ensures that each cell receives the oxygen it needs to function properly.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the structure, function, and evolution of tracheal systems. We’ll uncover how these organisms transport oxygen and carbon dioxide, and discover the adaptations that have enabled them to thrive in various habitats. So, buckle up and join us on this captivating journey into the realm of tracheal systems!
An organism with a tracheal system, like an insect, relies on a network of tubes to breathe. This efficient respiratory system allows them to thrive in various environments. Similarly, an indoor vertical farming system for efficient quality food production utilizes a controlled environment to optimize plant growth.
By mimicking nature’s efficiency, this system ensures a reliable supply of fresh, high-quality produce, just like the oxygen-rich environment provided by a tracheal system.
1. Introduction
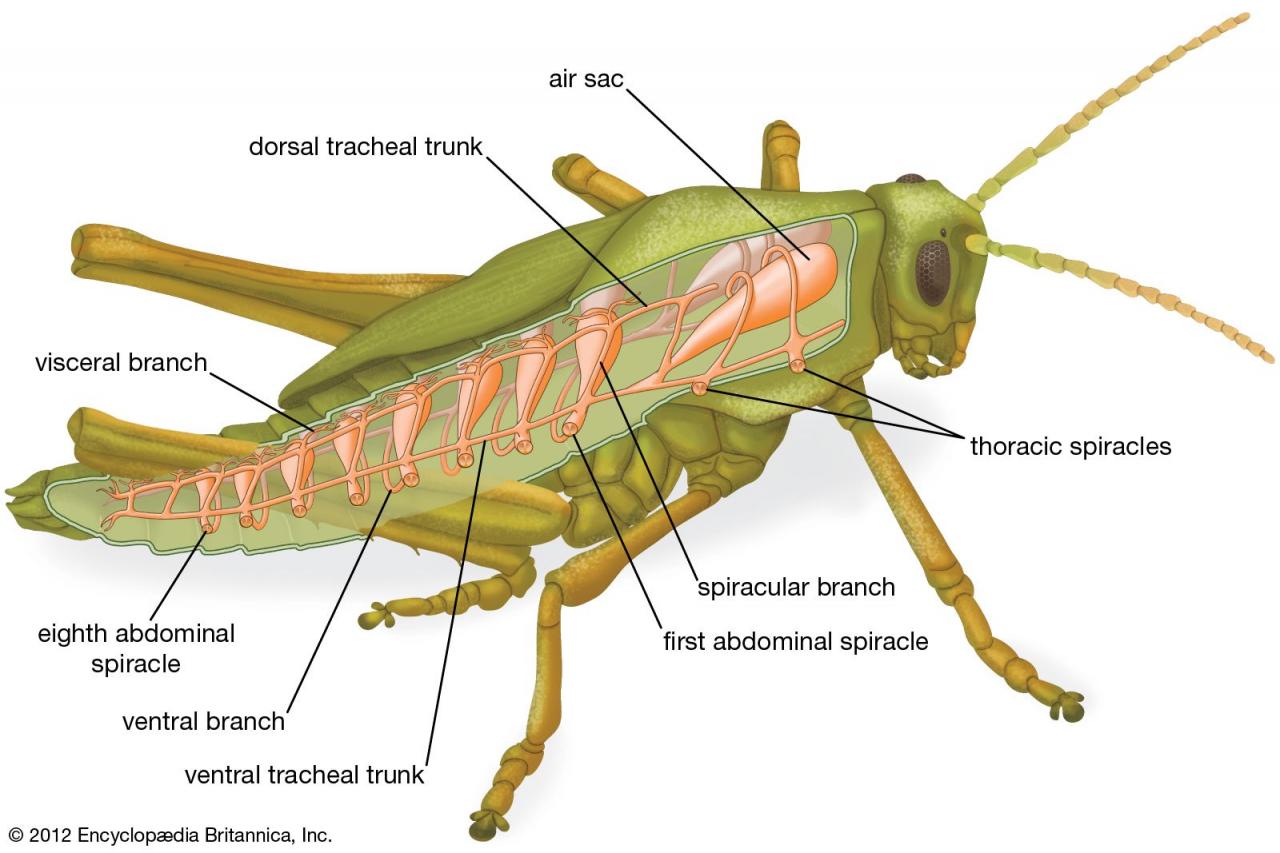
A tracheal system is a network of tubes that allows for the exchange of gases between an organism and its environment. It is found in insects, arachnids, and myriapods, and is essential for their survival. The tracheal system is composed of a series of branching tubes that connect to spiracles, which are small openings on the body surface.
An organism with a tracheal system, like an insect, breathes through a network of tubes that carry oxygen directly to its cells. Similarly, an operating system is the core software that manages the hardware and software resources of a computer, allowing different programs to run smoothly.
Just as the tracheal system ensures the proper functioning of an organism, an operating system provides the foundation for a computer to perform its tasks efficiently. Understanding the fundamentals of an operating system, as explained in an introduction to operating systems , is essential for anyone who wants to delve into the world of computing.
Air enters the spiracles and travels through the tubes to the tracheoles, which are the smallest branches of the tracheal system. The tracheoles deliver oxygen to the cells and remove carbon dioxide.
Organisms with tracheal systems, like insects, have complex respiratory systems that allow them to breathe efficiently. The transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide through these systems can be described using transfer entropy, a concept that measures the flow of information between different parts of a complex system.
An introduction to transfer entropy information flow in complex systems provides a detailed overview of this concept and its applications in understanding the dynamics of biological systems like those found in organisms with tracheal systems.
2. Structure of the Tracheal System: An Organism With Tracheal System
The tracheal system is a complex network of tubes that branch throughout the body of an insect. The main trunk of the tracheal system is called the trachea, which runs along the dorsal side of the body. The trachea gives rise to a series of smaller tubes called bronchi, which in turn give rise to even smaller tubes called tracheoles.
An organism with a tracheal system, like an insect, breathes through tiny tubes that carry oxygen directly to its cells. Similarly, an ideal education system would provide a direct and tailored learning experience for each student, ensuring that their unique needs are met.
Just as the tracheal system delivers oxygen to every corner of an insect’s body, an ideal education system would deliver knowledge and skills to every corner of a student’s mind.
The tracheoles are the smallest branches of the tracheal system and they extend to all parts of the body, even to the individual cells.
An organism with a tracheal system, like an insect, breathes through a network of tubes that carry oxygen directly to its cells. In a similar vein, an inventory planning system that schedules the precise quantity ensures that each cell in the supply chain receives the exact amount of oxygen – or inventory – it needs to function efficiently.
Components of the Tracheal System, An organism with tracheal system
- Trachea:The main trunk of the tracheal system that runs along the dorsal side of the body.
- Bronchi:Smaller tubes that branch off from the trachea and extend to different parts of the body.
- Tracheoles:The smallest branches of the tracheal system that extend to all parts of the body, even to the individual cells.
- Spiracles:Small openings on the body surface that allow air to enter and exit the tracheal system.
3. Function of the Tracheal System
The tracheal system is responsible for the exchange of gases between an insect and its environment. Oxygen enters the spiracles and travels through the tubes to the tracheoles, which deliver oxygen to the cells. Carbon dioxide is produced by the cells and travels back through the tracheoles to the spiracles, where it is released into the environment.
Gas Exchange in the Tracheal System
- Oxygen uptake:Oxygen enters the spiracles and travels through the tubes to the tracheoles, which deliver oxygen to the cells.
- Carbon dioxide removal:Carbon dioxide is produced by the cells and travels back through the tracheoles to the spiracles, where it is released into the environment.
Final Summary
As we conclude our exploration of organisms with tracheal systems, we’re left in awe of the intricate adaptations and evolutionary marvels that have shaped these creatures. The tracheal system stands as a testament to the diversity and resilience of life on Earth.
Its ability to facilitate efficient gas exchange has allowed organisms to conquer a wide range of environments, from the depths of the ocean to the soaring heights of the sky.
The study of tracheal systems continues to captivate scientists and researchers, offering valuable insights into the evolution and physiology of living organisms. As we delve deeper into the mysteries of these fascinating creatures, we can’t help but marvel at the wonders of nature and the boundless possibilities that lie ahead.
FAQ Compilation
What is a tracheal system?
An organism with a tracheal system, like an insect, relies on a network of tubes to transport oxygen throughout its body. Much like the way an integrated labor management system for taco bell automates processes and optimizes scheduling , the tracheal system efficiently delivers oxygen to every cell in the organism’s body.
A tracheal system is a network of tubes that transport oxygen directly to the body’s tissues and remove carbon dioxide.
How does the tracheal system work?
Air enters the body through openings called spiracles and travels through the trachea, bronchi, and tracheoles to reach the body’s cells.
What are the advantages of a tracheal system?
Tracheal systems are highly efficient and allow for rapid gas exchange, making them ideal for active organisms.
Just like an organism with a tracheal system, an operating system also needs a well-functioning system to thrive. An operating system change that fixes bugs improves security , just like how a healthy tracheal system allows an organism to breathe efficiently.
With an improved operating system, an organism with a tracheal system can function optimally.
An organism with a tracheal system breathes through small tubes called tracheae. Like the tiny sensors and actuators in an introduction to mems microelectromechanical systems , these tracheae allow for efficient gas exchange, keeping the organism alive and kicking.