An introduction to multiagent systems 2nd edition – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of multiagent systems! This comprehensive guide, An Introduction to Multiagent Systems: 2nd Edition, delves into the intricate world where multiple agents interact, communicate, and collaborate to achieve common goals.
This book, “An Introduction to Multiagent Systems, 2nd Edition,” provides a comprehensive overview of multiagent systems, including their concepts, models, and applications. These systems have gained significant attention in recent years, particularly in the context of indoor vertical farming systems for efficient quality food production.
An indoor vertical farming system leverages controlled environments and advanced technologies to optimize crop growth and yield. By integrating multiagent systems into such systems, farmers can enhance decision-making, resource allocation, and overall efficiency, ultimately contributing to sustainable and reliable food production.
However, the broader applications of multiagent systems extend far beyond indoor farming, making this book an invaluable resource for anyone interested in the field.
Dive deep into the foundations of multiagent systems, exploring their unique characteristics, real-world applications, and the diverse types of agents that populate this dynamic landscape. Understand the strengths and limitations of different agent architectures, and witness the power of communication and coordination in orchestrating effective multiagent systems.
1. Overview of Multiagent Systems
Multiagent systems (MAS) are systems composed of multiple autonomous agents that interact with each other to achieve a common goal or set of goals. Agents are entities that can sense their environment, make decisions, and act to achieve their goals.
MAS are becoming increasingly popular in a wide variety of applications, including robotics, distributed computing, and artificial intelligence.Some real-world applications of MAS include:
-
-*Swarm robotics
An Introduction to Multiagent Systems 2nd Edition delves into the intricate world of autonomous agents, exploring their interactions and collective behaviors. From the operating systems that power our devices to the example of system software that orchestrates complex processes, the study of multiagent systems sheds light on the underlying mechanisms that govern these sophisticated technological ecosystems.
As we delve deeper into this captivating field, we uncover the fundamental principles that shape the interactions between autonomous agents, empowering us to harness their collective intelligence for solving real-world challenges.
A group of robots that work together to perform a task, such as cleaning a floor or searching for a lost object.
-*Distributed computing
An Introduction to Multiagent Systems 2nd Edition is a must-read for anyone interested in the field. It provides a comprehensive overview of the latest research and developments in multiagent systems, including topics such as an erp system is and agent-based modeling.
The book is well-written and easy to follow, making it an ideal resource for both students and researchers.
A network of computers that work together to solve a problem, such as weather forecasting or protein folding.
-*Artificial intelligence
A system that can learn and reason, such as a self-driving car or a medical diagnosis system.
2. Types of Agents
There are many different types of agents, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common types of agents include:
-
-*Reactive agents
The second edition of An Introduction to Multiagent Systems is a comprehensive guide to the field, covering everything from the basics to the latest advances. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced researcher, this book has something for you. And if you’re looking for a break from the technical stuff, check out this fascinating article about an icy small solar system body . It’s a great reminder that there’s still so much we don’t know about our universe.
But back to the book, An Introduction to Multiagent Systems is a must-read for anyone interested in this exciting field.
These agents react to their environment without any planning or reasoning. They are typically used in simple applications, such as traffic lights or thermostats.
-*Deliberative agents
These agents plan their actions before they execute them. They are typically used in more complex applications, such as chess-playing programs or self-driving cars.
-*Hybrid agents
These agents combine elements of both reactive and deliberative agents. They can react to their environment while also planning their actions. Hybrid agents are often used in applications that require both speed and flexibility.
3. Agent Architectures: An Introduction To Multiagent Systems 2nd Edition
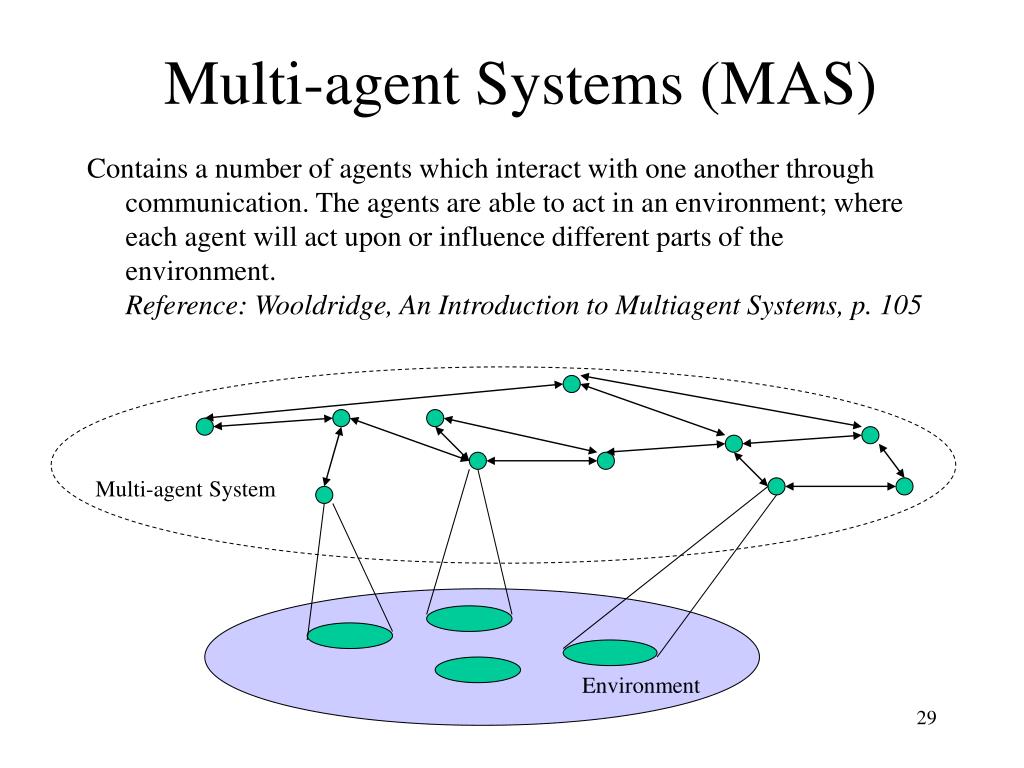
There are many different agent architectures, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common agent architectures include:
-
-*Reactive architectures
These architectures are based on the idea that agents should react to their environment without any planning or reasoning. Reactive architectures are typically used in simple applications, such as traffic lights or thermostats.
-*Deliberative architectures
An Introduction to MultiAgent Systems 2nd Edition delves into the fascinating world of multiagent systems, exploring their principles, architectures, and applications. Just like an internal control system consists of the policies and procedures that govern an organization’s operations, multiagent systems rely on a set of rules and protocols to coordinate and collaborate.
This comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of the concepts and techniques involved in designing, implementing, and evaluating multiagent systems, empowering you to harness their potential in a wide range of real-world scenarios.
These architectures are based on the idea that agents should plan their actions before they execute them. Deliberative architectures are typically used in more complex applications, such as chess-playing programs or self-driving cars.
-*Hybrid architectures
These architectures combine elements of both reactive and deliberative architectures. Hybrid architectures are often used in applications that require both speed and flexibility.
4. Communication and Coordination
Communication and coordination are essential for multiagent systems to achieve their goals. There are many different methods of communication and coordination, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common methods of communication and coordination include:
-
-*Direct communication
Whether you’re a seasoned multiagent systems pro or just starting out with the basics, “An Introduction to Multiagent Systems, 2nd Edition” is your go-to guide. Dive into the latest research and applications, from cooperative problem-solving to the hot topic of artificial intelligence.
And while you’re exploring the intricacies of multiagent systems, don’t forget to check out an essay on the revived Bretton Woods system for a fresh perspective on global economic policy. “An Introduction to Multiagent Systems, 2nd Edition” will keep you on the cutting edge of this exciting field.
Agents send messages directly to each other.
-*Indirect communication
An Introduction to MultiAgent Systems, 2nd Edition delves into the complexities of multiagent systems, providing a comprehensive guide to their design, implementation, and analysis. However, if you encounter the dreaded error message, “an error occurred. please contact your system administrator,” an error occurred.
please contact your system administrator. , don’t panic. Simply follow the troubleshooting steps provided and you’ll be back on track to exploring the fascinating world of multiagent systems.
Agents send messages to each other through a central server or message broker.
-*Coordination mechanisms
In the realm of multiagent systems, the intricacies of coordination and collaboration take center stage. Just like in the human body, where organs like the heart and lungs work harmoniously to sustain life, multiagent systems require seamless coordination among their agents.
To explore this fascinating analogy further, check out an example of the organ system level of organization . It sheds light on the parallels between biological systems and the coordination challenges faced in multiagent systems. By delving into this topic, you’ll gain valuable insights into the principles that govern both biological and artificial systems, unlocking the potential for more efficient and collaborative multiagent designs.
Agents use coordination mechanisms to coordinate their actions. Coordination mechanisms can be either centralized or decentralized.
5. Cooperation and Competition
Cooperation and competition are two fundamental aspects of multiagent systems. Cooperation occurs when agents work together to achieve a common goal. Competition occurs when agents compete with each other to achieve their own goals.There are many different types of cooperation and competition, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Some of the most common types of cooperation and competition include:
-
-*Pure cooperation
Agents work together to achieve a common goal without any competition.
-*Mixed cooperation
Agents cooperate with each other to achieve a common goal, but they also compete with each other to achieve their own goals.
-*Pure competition
Agents compete with each other to achieve their own goals without any cooperation.
6. Learning and Adaptation
Learning and adaptation are essential for multiagent systems to be able to operate in a changing environment. There are many different types of learning and adaptation algorithms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common types of learning and adaptation algorithms include:
-
-*Supervised learning
Agents learn from a set of labeled data.
-*Unsupervised learning
In “An Introduction to Multiagent Systems, 2nd Edition,” you’ll learn how to model and analyze systems where multiple agents interact. This knowledge can be applied to a wide range of domains, including robotics, economics, and even the human immune system.
When the immune system overreacts, it can cause an exaggerated response known as an exaggerated response by the immune system . Understanding how to model and control such systems is essential for developing effective treatments for autoimmune diseases.
Agents learn from a set of unlabeled data.
-*Reinforcement learning
Agents learn from their interactions with the environment.
7. Applications of Multiagent Systems
Multiagent systems are being used in a wide variety of applications, including:
-
-*Robotics
Multiagent systems are used to control teams of robots that work together to perform tasks, such as cleaning a floor or searching for a lost object.
-*Distributed computing
Multiagent systems are used to distribute tasks across a network of computers, such as weather forecasting or protein folding.
-*Artificial intelligence
Multiagent systems are used to create intelligent systems that can learn and reason, such as self-driving cars or medical diagnosis systems.
Last Word
As we conclude our exploration of multiagent systems, it becomes evident that these systems hold immense potential for solving complex problems and transforming industries. From healthcare to transportation, from finance to manufacturing, the applications of multiagent systems are vast and ever-expanding.
This guide has provided a comprehensive introduction to the field, equipping you with the knowledge and understanding to navigate the challenges and harness the opportunities presented by multiagent systems. Embrace the future of collaboration and innovation as you delve deeper into this fascinating and rapidly evolving domain.
Popular Questions
What are the key characteristics of multiagent systems?
Multiagent systems are characterized by autonomy, social ability, reactivity, pro-activeness, and learning.
What are some real-world applications of multiagent systems?
Multiagent systems find applications in various domains, including robotics, traffic management, resource allocation, and distributed problem solving.
What are the different types of agents in multiagent systems?
Agents in multiagent systems can be classified based on their characteristics, such as reactive agents, deliberative agents, and hybrid agents.
What is the importance of communication and coordination in multiagent systems?
Communication and coordination are crucial for enabling agents to share information, coordinate their actions, and achieve common goals.
How can multiagent systems be used to solve complex problems?
Multiagent systems can be employed to solve complex problems by leveraging the collective intelligence and collaboration of multiple agents.