An atom with a net electric charge, a captivating subject that unveils the intriguing world of atoms carrying an electrical imbalance, takes center stage in this captivating exploration. Prepare to delve into the fascinating realm of charged atoms, where electrons and protons dance in a delicate balance, shaping the very nature of matter.
An atom with a net electric charge, also known as an ion, can be used in various applications. One such application is in a transformer, an electrical device used for voltage conversion. The ion’s ability to carry charge allows it to interact with electromagnetic fields, facilitating the transfer of energy between circuits.
Uncover the secrets of how atoms acquire or shed electrons, resulting in a net electric charge. Discover the diverse types of electrically charged atoms, from ions to radicals, each possessing unique characteristics and properties. Explore the profound significance of charged atoms in shaping chemical reactions, electrical phenomena, and countless other processes that govern our world.
An atom with a net electric charge, also known as an ion, can attract or repel other charged particles. Similarly, a water molecule has an electric dipole , meaning it has a positive end and a negative end. This polarity allows water molecules to interact with each other and with other molecules, forming hydrogen bonds and creating the unique properties of water.
The net electric charge of an atom, therefore, plays a crucial role in determining the behavior of molecules and their interactions with the surrounding environment.
Definition of an Atom with a Net Electric Charge
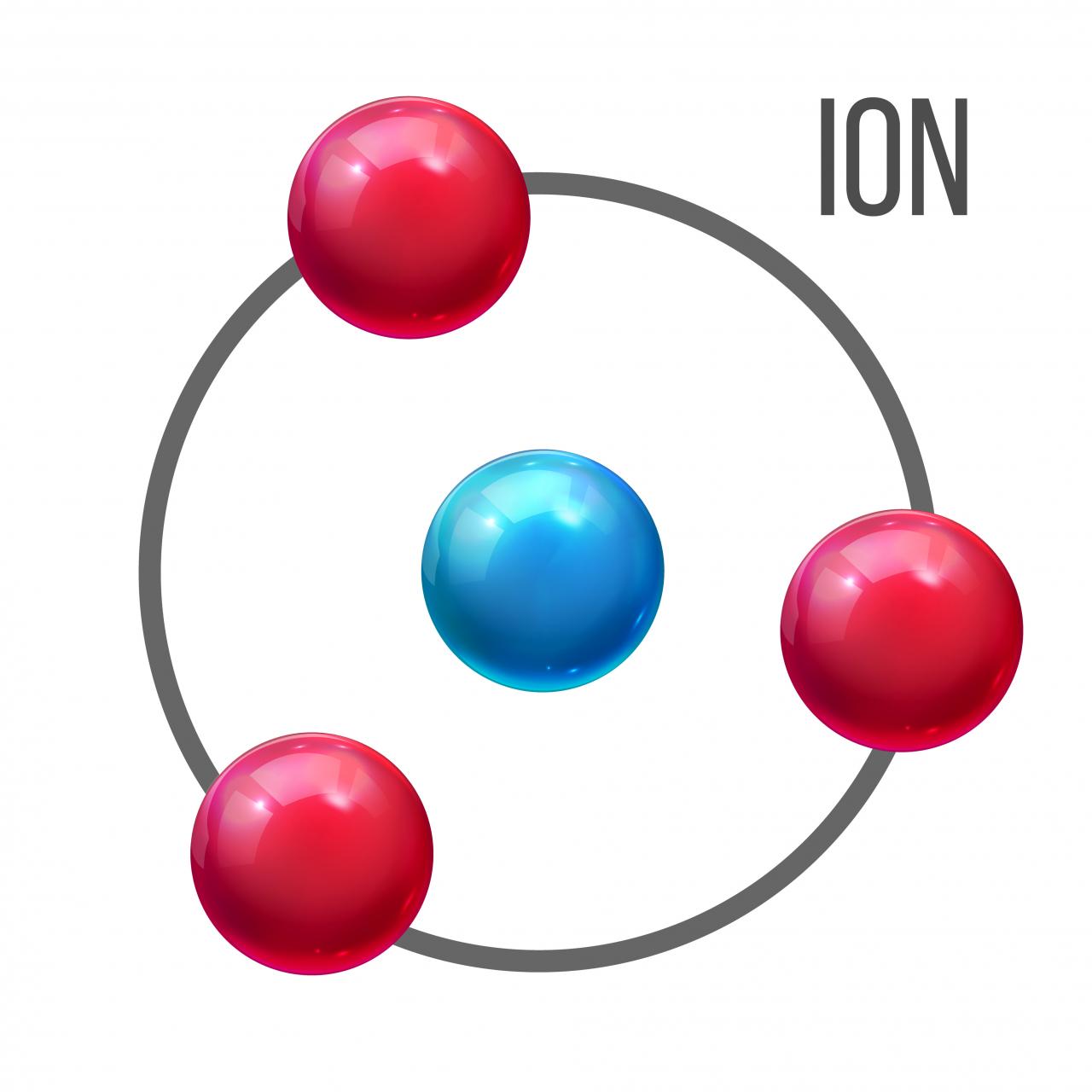
An atom is the fundamental building block of matter. It consists of a nucleus, which contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The number of protons and electrons in an atom are normally equal, resulting in a net electric charge of zero.
An atom with a net electric charge is like a power source that creates a circuit. The circuit is an uninterrupted electrical path for current flow , allowing electricity to flow freely. Just like the charge in an atom, this path ensures that the current has a clear and consistent way to travel.
However, when an atom gains or loses electrons, it acquires a net electric charge.
Causes of a Net Electric Charge in an Atom
The electric charge of an atom is determined by the number of electrons it has compared to the number of protons. When an atom has more electrons than protons, it has a net negative charge and is called an anion.
Like an atom with a net electric charge, an electronic system relies on the delicate balance of electrical currents. Manufacturers utilize electrical fuses to safeguard these systems, ensuring that excessive current doesn’t disrupt the flow of electrons, just as an atom’s net charge influences its chemical behavior.
Conversely, when an atom has more protons than electrons, it has a net positive charge and is called a cation.Atoms can gain or lose electrons through various processes, such as chemical reactions, ionization, or electron capture. In chemical reactions, atoms can transfer electrons to or from other atoms, resulting in a change in their electric charge.
Ionization occurs when an atom loses or gains an electron due to the absorption or emission of energy, such as heat or light. Electron capture is a process where an atom captures an electron from its surroundings, leading to a decrease in its net positive charge.
Yo, check it out, an atom with a net electric charge is like a party in a power plant, it’s got some extra juice. And if you’re feeling crafty, you can even add a hand pump to an electric well, just like this awesome tutorial shows you.
But don’t forget, our atomic buddy with the extra charge is still the star of the show, bringing the energy like nobody’s business.
Types of Atoms with a Net Electric Charge
There are two main types of atoms with a net electric charge: ions and radicals. Ions are atoms that have lost or gained one or more electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Radicals are atoms or molecules that have unpaired electrons, giving them a net magnetic moment.
Significance of Atoms with a Net Electric Charge
Atoms with a net electric charge play a crucial role in various chemical and physical processes. They are involved in chemical bonding, which holds atoms together to form molecules and compounds. Net electric charges also contribute to electrical conductivity, allowing materials to conduct electricity.
When an atom has a net electric charge, it’s like a superhero with a secret power. And just like superheroes have gadgets to measure their abilities, scientists use an ammeter to measure the electric charge flowing through a circuit. But even without an ammeter, you can feel the electric charge in the air, like the static electricity that makes your hair stand on end.
It’s a reminder that even the smallest particles can pack a punch.
Additionally, atoms with a net electric charge are essential for many biological processes, such as nerve impulses and muscle contractions.
An atom with a net electric charge, also known as an ion, can be compared to the addition of a switch to an electrical outlet. Adding a switch allows for convenient control of the electrical flow, just like an ion’s charge influences its chemical and physical properties.
Measurement and Detection of Net Electric Charge in Atoms, An atom with a net electric charge
The net electric charge of atoms can be measured using various techniques, including electrophoresis, mass spectrometry, and atomic force microscopy. Electrophoresis is a method that separates charged molecules based on their mobility in an electric field. Mass spectrometry measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions, allowing for the determination of their electric charge.
Atomic force microscopy can be used to image the surface of materials and measure the electric charge of individual atoms.
Wrap-Up: An Atom With A Net Electric Charge
As we conclude our journey into the realm of atoms with a net electric charge, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate interplay between electrons and protons. These charged atoms play a pivotal role in shaping the chemical and physical world around us, from the formation of molecules to the conduction of electricity.
Understanding their behavior empowers us to harness their potential in diverse applications, unlocking new frontiers in science and technology.
FAQ
What is the significance of atoms with a net electric charge?
Atoms with a net electric charge play a crucial role in various chemical and physical processes, including chemical bonding, electrical conductivity, and many others. They contribute to the formation of molecules, the flow of electricity, and countless phenomena that shape our world.
How can atoms acquire or lose electrons?
Atoms can acquire or lose electrons through various mechanisms, such as chemical reactions, ionization, and electron transfer processes. These processes can result in the formation of positively or negatively charged atoms, depending on whether electrons are gained or lost.