An atom is electrically neutral how can it become charged – An atom is electrically neutral, meaning it has an equal number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons. But how can this neutral entity become charged? Dive into the electrifying world of atoms and discover the secrets behind their ability to gain or lose electrons, transforming them from neutral spectators to charged participants in the chemical dance.
Atoms are electrically neutral, but they can become charged when they gain or lose electrons. One way to charge an atom is by using an electric current, like the one that powers an electric car. Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular because they offer a number of advantages over gasoline-powered cars, including lower operating costs, reduced emissions, and improved performance.
To learn more about the advantages of owning an electric car, click here . When an atom loses an electron, it becomes positively charged. When an atom gains an electron, it becomes negatively charged.
Through the processes of ionization and electron gain, atoms shed or acquire electrons, tipping the balance of their electrical neutrality. Let’s unravel the mysteries of these transformations and explore the factors that influence an atom’s charging capabilities.
An atom is electrically neutral, but it can become charged by gaining or losing electrons. This process is called ionization. When an atom loses an electron, it becomes positively charged. When an atom gains an electron, it becomes negatively charged.
This is similar to adding a circuit to an electrical panel. Add a circuit to increase the number of electrical outlets in a room. When you add a circuit, you are essentially creating a new path for electricity to flow.
This allows you to plug in more devices without overloading the electrical system.
An Atom is Electrically Neutral: How Can it Become Charged?
Atoms, the building blocks of matter, are generally electrically neutral, meaning they have no overall electrical charge. However, under certain conditions, atoms can lose or gain electrons, resulting in a charged state.
Normally, an atom is electrically neutral. How can it become charged? It’s kind of like what happens when you put a 20 lb turkey in an electric roaster . The heat causes the atoms to gain or lose electrons, giving them a charge.
Understanding Electrical Neutrality, An atom is electrically neutral how can it become charged
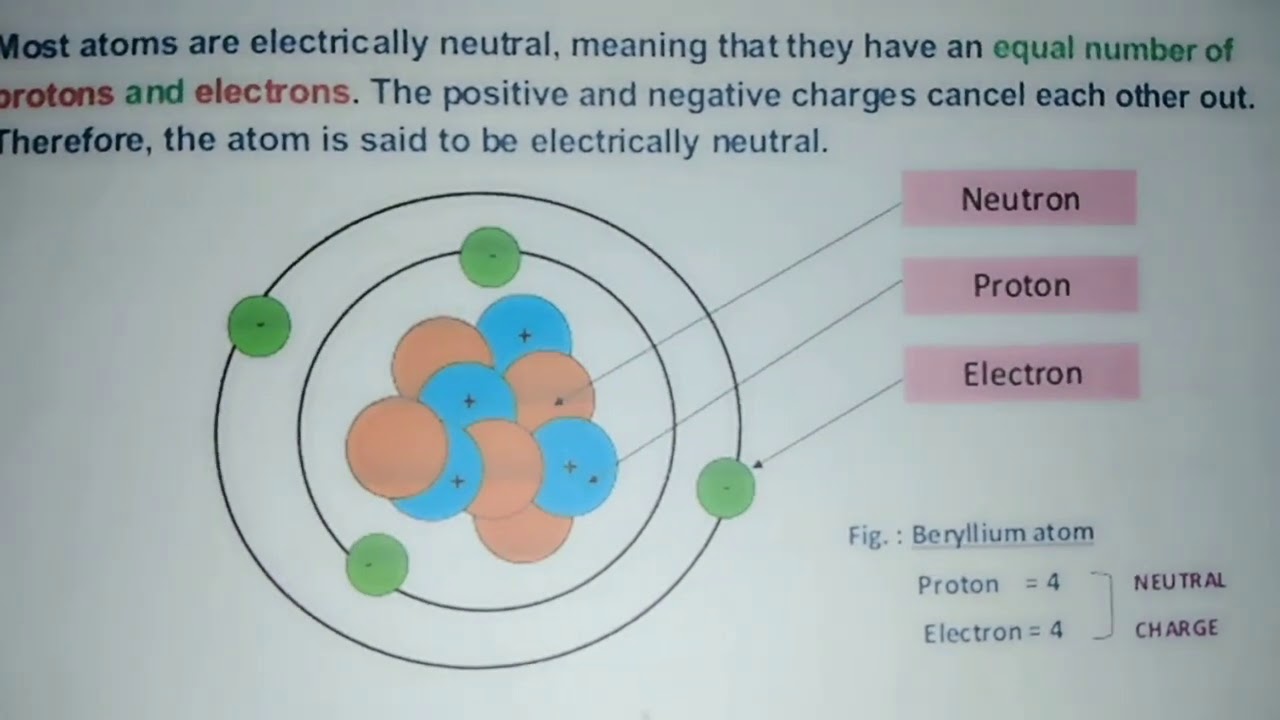
Electrical neutrality in atoms stems from the equal number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons they contain. Protons reside in the atom’s nucleus, while electrons orbit around it. The positive and negative charges cancel each other out, resulting in a neutral overall charge.
Atoms start off neutral, but they can gain or lose electrons to become charged. This is like how an electrical advertising sign uses charged particles to light up. Read a rhyme about an electrical advertising sign to learn more about how electricity works.
When an atom loses an electron, it becomes positively charged. When it gains an electron, it becomes negatively charged. This is how atoms can become charged.
Ionization and Loss of Electrons
Ionization occurs when an atom loses one or more electrons, creating a positively charged ion. This process typically occurs when an atom interacts with a high-energy source, such as heat or radiation, which provides enough energy to overcome the electron’s attraction to the nucleus.
Normally an atom is electrically neutral. But it can become charged. For instance, if you add an extra electrical outlet , you could change the voltage in the circuit and cause an atom to gain or lose electrons, resulting in a charged atom.
Positive ions have fewer electrons than protons, resulting in a net positive charge. For example, when sodium loses an electron, it becomes a positively charged sodium ion (Na+).
Gaining Electrons and Charging
Atoms can also gain electrons, resulting in a negatively charged ion. This process is known as electron affinity and occurs when an atom has a strong attraction for electrons. Atoms with a high electron affinity are more likely to gain electrons.
Atoms are electrically neutral, but they can become charged by gaining or losing electrons. When an electric current flows through a material, it can cause electrons to move, which can result in changes in the electrical charge of atoms. Three effects of an electric current include heating, chemical changes, and magnetic fields.
These effects are all caused by the movement of electrons, which can change the electrical charge of atoms.
Negative ions have more electrons than protons, giving them a net negative charge. For instance, when chlorine gains an electron, it becomes a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl-).
Since an atom is electrically neutral, it can become charged by adding or removing electrons. Think of it like adding an electrical outlet from a light switch adding an electrical outlet from a light switch . If you connect the wires correctly, you’ll have a new outlet to power your devices.
Similarly, adding or removing electrons changes the electrical charge of an atom.
Factors Affecting Charging
Several factors influence an atom’s ability to become charged:
- Atomic size:Larger atoms have a weaker attraction for their electrons, making them more likely to lose electrons and become positive ions.
- Electronegativity:Electronegativity measures an atom’s ability to attract electrons. Atoms with high electronegativity are more likely to gain electrons and become negative ions.
- Ionization energy:Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. Atoms with high ionization energy are less likely to lose electrons and become positive ions.
Consequences of Charging
Charged atoms have significant consequences in chemical reactions and processes:
- Chemical bonding:Charged atoms can form ionic bonds with oppositely charged ions, resulting in the formation of ionic compounds.
- Reactivity:Charged atoms are more reactive than neutral atoms, as they have a stronger attraction or repulsion towards other charged species.
- Chemical reactions:Charged atoms participate in chemical reactions by transferring electrons to or from other atoms or ions, facilitating chemical transformations.
Ending Remarks: An Atom Is Electrically Neutral How Can It Become Charged
As atoms become charged, they enter a new realm of chemical interactions. Their altered electrical nature affects their bonding abilities and reactivity, opening up a vast playground for chemical reactions. Understanding the mechanisms of charging empowers us to predict and manipulate the behavior of atoms, paving the way for advancements in fields such as materials science, electronics, and energy storage.
Key Questions Answered
What happens when an atom loses an electron?
When an atom loses an electron, it becomes positively charged, forming a positively charged ion known as a cation.
How do atoms gain electrons?
Atoms gain electrons through a process called electron affinity, where they attract and bind additional electrons, resulting in a negatively charged ion called an anion.
What factors influence an atom’s ability to become charged?
Factors such as atomic size, electronegativity, and ionization energy play crucial roles in determining an atom’s propensity to gain or lose electrons, thus affecting its charging capabilities.