Basic parts of an electric generator – Delve into the captivating world of electric generators, where mechanical energy transforms into electrical power. Unravel the intricacies of their basic components, exploring their functions and how they orchestrate the magic of electricity generation.
An electric generator’s basic parts include the armature, which rotates within the stator, creating a magnetic field. Just like how an electric motor contains two electromagnets , a generator uses a rotating magnetic field to generate electricity. The armature’s rotation induces a current in the stator windings, which is then converted into usable electrical power.
From the stator’s magnetic embrace to the rotor’s dynamic dance, each part plays a vital role in this electrifying symphony. Prepare to be amazed as we embark on a journey into the heart of an electric generator.
The basic parts of an electric generator include a rotor, stator, and field windings. These components work together to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. For electric car owners, understanding these basics can help them calculate the average cost of charging their vehicles in the UK.
You can find more information about this by visiting average cost of charging an electric car uk . Returning to the topic of generators, the efficiency of these devices is crucial for maximizing power output.
Components of an Electric Generator
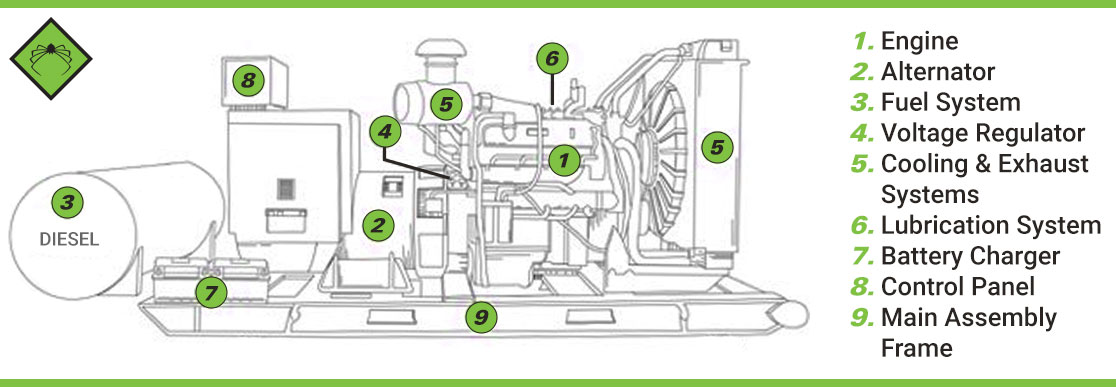
Electric generators are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. They consist of several key components that work together to produce electricity.
Yo, check it! Electric generators, the OG powerhouses, are made up of a few key parts. The stator’s the main dude, generating electricity when the rotor spins like a top. If you’re having trouble with an electric power tool acting up at Home Depot , it could be a stator issue.
But hey, back to generators: the rotor’s the spinning part, and the field windings create the magnetic field that makes the whole thing work. It’s like a party in there!
The main components of an electric generator include:
- Stator:The stator is the stationary part of the generator that contains the armature windings. These windings are made of copper wire and are arranged in slots on the stator’s core. When the rotor spins inside the stator, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the armature windings to produce electricity.
- Rotor:The rotor is the rotating part of the generator that contains the field windings. These windings are also made of copper wire and are connected to a source of direct current (DC). The field windings create a magnetic field that interacts with the armature windings to produce electricity.
- Field winding:The field winding is the winding on the rotor that creates the magnetic field. It is connected to a source of DC power, which creates a magnetic field around the rotor.
- Armature winding:The armature winding is the winding on the stator that is connected to the electrical load. It is made up of a series of coils of wire that are wound around the stator’s core. When the rotor spins, it creates a changing magnetic field that induces a voltage in the armature winding.
If you’re curious about the ins and outs of an electric generator, you’ll want to know about its basic parts. The stator, rotor, and armature are key components that work together to generate electricity. And if you’re thinking about upgrading your home’s electrical system, you may want to consider the average cost for an electrical panel replacement . It’s a good idea to have a professional electrician inspect your electrical panel to ensure it’s up to code and can handle the demands of your home’s electrical needs.
Getting back to electric generators, the field coils and prime mover are also important parts that contribute to the generation of electricity.
Types of Electric Generators: Basic Parts Of An Electric Generator
There are two main types of electric generators: DC generators and AC generators.
The stator, rotor, and field windings are the basic parts of an electric generator. These components work together to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. If you’re interested in learning more about electric bikes, the average cost of an electric bike in the UK is around £1,500. Returning to electric generators, the armature is another important component that helps generate electricity.
DC generatorsproduce direct current (DC), which flows in one direction only. They are typically used in applications where a constant voltage is required, such as in battery charging systems.
The basic parts of an electric generator include the rotor, stator, and field windings. The rotor spins inside the stator, and the field windings create a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor’s windings to generate electricity. An electrolytic cell uses electrical energy to drive a chemical reaction, which can be used to produce hydrogen or other chemicals.
The basic parts of an electric generator are essential for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
AC generatorsproduce alternating current (AC), which reverses direction periodically. They are typically used in applications where a varying voltage is required, such as in power plants and electric motors.
Working Principle of an Electric Generator
The basic principle of an electric generator is electromagnetic induction. When a conductor is moved through a magnetic field, it experiences an electromotive force (EMF), which is a voltage. This EMF can be used to drive current through a circuit, producing electricity.
The basic parts of an electric generator include the stator, rotor, and armature. These components work together to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. An electric motor, on the other hand, converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. For instance, an electric motor lifts an elevator that weighs 1.20 . The basic parts of an electric generator are essential for understanding how these devices generate electricity.
In an electric generator, the rotor is spun inside the stator, creating a changing magnetic field. This changing magnetic field induces an EMF in the armature windings, which are connected to the electrical load. The EMF causes current to flow through the load, producing electricity.
An electric generator’s basic parts include a stator, rotor, and field coils. These components work together to create an electrical circuit. As you know, an electrical circuit must contain a complete path for electrons to flow. In an electric generator, the stator and rotor create a changing magnetic field, which induces an electrical current in the field coils.
Design Considerations for Electric Generators
When designing an electric generator, there are several key factors to consider, including:
- Voltage:The voltage of the generator is the difference in electrical potential between the two terminals of the generator. It is important to choose a generator with a voltage that is compatible with the electrical load.
- Current:The current of the generator is the amount of electrical current that the generator can produce. It is important to choose a generator with a current that is sufficient for the electrical load.
- Power output:The power output of the generator is the amount of electrical power that the generator can produce. It is important to choose a generator with a power output that is sufficient for the electrical load.
- Efficiency:The efficiency of the generator is the ratio of the electrical power output to the mechanical power input. It is important to choose a generator with a high efficiency to minimize losses.
Applications of Electric Generators
Electric generators are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Power plants:Electric generators are used in power plants to convert mechanical energy from turbines into electrical energy. This electricity is then distributed to homes and businesses.
- Transportation:Electric generators are used in vehicles to charge the battery and power the electrical systems. They are also used in hybrid and electric vehicles to generate electricity to power the motor.
- Backup power systems:Electric generators are used as backup power systems in homes and businesses to provide electricity in the event of a power outage.
Troubleshooting Electric Generators
Electric generators can experience a variety of problems, including:
- No output:This can be caused by a variety of problems, including a faulty stator, rotor, or field winding.
- Low output:This can be caused by a variety of problems, including a weak magnetic field, a dirty armature, or a loose connection.
- Overheating:This can be caused by a variety of problems, including a faulty bearing, a blocked cooling system, or a high load.
To troubleshoot an electric generator, it is important to first identify the problem. Once the problem has been identified, it can be repaired or replaced.
Maintenance and Safety for Electric Generators
Electric generators require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This maintenance includes:
- Cleaning:The generator should be cleaned regularly to remove dirt and debris. This will help to prevent overheating and other problems.
- Lubrication:The generator should be lubricated regularly to ensure that all moving parts are operating smoothly. This will help to prevent wear and tear.
- Inspection:The generator should be inspected regularly for any signs of damage. This will help to identify potential problems early on.
When operating an electric generator, it is important to follow all safety precautions. These precautions include:
- Never operate a generator indoors:Generators produce carbon monoxide, which is a poisonous gas. Operating a generator indoors can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Keep the generator away from flammable materials:Generators can produce sparks, which can ignite flammable materials.
- Never touch the generator with wet hands:Generators can produce electricity, which can shock you if you touch them with wet hands.
Last Point
Our exploration of the basic parts of an electric generator culminates in a profound appreciation for the intricate interplay of these components. Understanding their functions empowers us to harness electrical energy for a multitude of applications, from powering our homes to propelling vehicles.
As we conclude this journey, let the knowledge gained serve as a beacon, illuminating the path towards further exploration and innovation in the realm of electricity generation.
FAQ
What is the primary function of a stator in an electric generator?
The basic parts of an electric generator include the stator, rotor, and field windings. The stator is the stationary part of the generator, while the rotor is the rotating part. The field windings create a magnetic field that interacts with the current in the stator windings to produce electricity.
An electrical current is continually seeking a pathway to the ground , and the generator provides that pathway by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The stator creates a stationary magnetic field, which interacts with the rotating magnetic field of the rotor to induce electrical current in the armature windings.
How does the rotor contribute to electricity generation?
The rotor generates a rotating magnetic field through the flow of direct current (DC) through its field windings. This rotating magnetic field interacts with the stator’s magnetic field to induce electrical current.
What is the role of armature windings in an electric generator?
Armature windings are conductors that are wound around the stator’s core. They are connected to the external circuit and carry the induced electrical current generated by the interaction of the stator and rotor magnetic fields.