An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy, powering everything from our household appliances to the electric vehicles that are revolutionizing transportation. In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of electric motors, exploring their inner workings, diverse applications, and the exciting advancements shaping their future.
An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. As the current flows through the coils, it creates a magnetic field which interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor, causing it to rotate. An electric motor contains two electromagnets and a rotor, which is a spinning part that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
The stator is the stationary part of the motor that contains the electromagnets.
Electric motors have become an indispensable part of our modern lives, silently and efficiently driving countless machines and devices. Understanding their fundamental principles and capabilities empowers us to appreciate the technological marvels that surround us.
An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. It’s like the heart of many appliances in our homes, including our electric kitchen ranges. An electric kitchen range has a total of four burners, each with its own heating element.
These heating elements convert electrical energy into heat, which is then transferred to the pots and pans we use to cook our food. An electric motor is a device which transforms, and it’s a key part of our modern kitchens.
Introduction
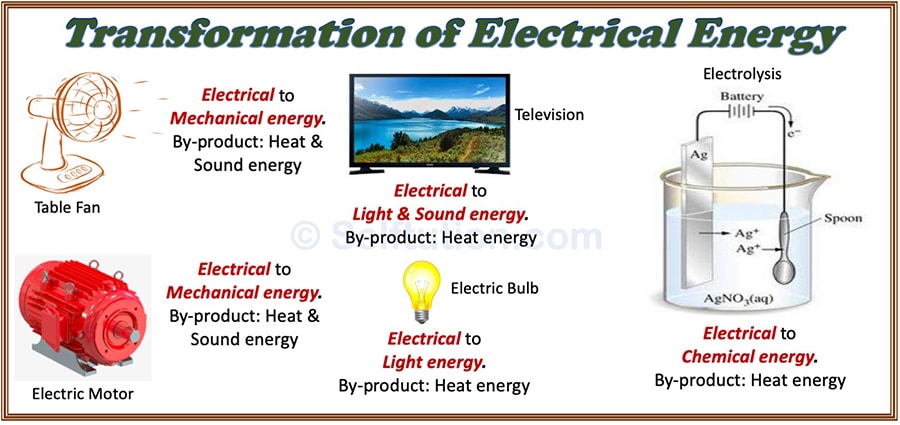
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is based on the principle of electromagnetism, where an electric current flowing through a conductor creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with a permanent magnet or another magnetic field to produce motion.
An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. For instance, an electric heater raises the temperature of 120g of water by converting electrical energy into heat energy. Similarly, an electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, enabling it to power various machines and devices.
Types of Electric Motors: An Electric Motor Is A Device Which Transforms
There are various types of electric motors, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some common types include:
- DC motors:Powered by direct current (DC), these motors offer high torque and speed control.
- AC motors:Powered by alternating current (AC), these motors are widely used due to their simplicity and reliability.
- Brushless motors:Eliminate the need for brushes, resulting in reduced maintenance and longer lifespan.
- Stepper motors:Offer precise control of angular movement, making them ideal for applications like robotics.
- Linear motors:Produce linear motion directly, without the need for gears or mechanical linkages.
Components of an Electric Motor
The main components of an electric motor include:
- Stator:The stationary part of the motor that creates a magnetic field.
- Rotor:The rotating part of the motor that interacts with the stator’s magnetic field to produce motion.
- Armature:The current-carrying conductor that generates the magnetic field on the rotor.
- Field winding:The coils that create the magnetic field on the stator.
- Commutator:A mechanical device that reverses the current flow in the armature to maintain continuous rotation (in DC motors).
Working Principle of an Electric Motor
When an electric current flows through the armature, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of the stator, causing the rotor to rotate. The direction of rotation depends on the direction of the current flow and the polarity of the magnetic fields.
An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. For example, an electric heater operating at 120 volts draws about 15 amps. And that’s because an electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors have a wide range of applications in various industries and devices, including:
- Industrial machinery:Powering pumps, compressors, conveyors, and other industrial equipment.
- Transportation:Driving electric vehicles, trains, and ships.
- Consumer appliances:Operating refrigerators, washing machines, and other household appliances.
- Robotics:Enabling precise movement and control in robotic systems.
- Medical devices:Powering surgical tools, diagnostic equipment, and patient monitoring devices.
Efficiency and Power of Electric Motors
The efficiency of an electric motor measures its ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Factors that affect efficiency include:
- Design and construction:Motor design and materials can impact efficiency.
- Load:The load on the motor can affect its efficiency.
- Operating conditions:Temperature, humidity, and other operating conditions can influence efficiency.
- Cleaning:Removing dust, dirt, and debris from the motor and its components.
- Lubrication:Lubricating moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- Inspections:Checking for any signs of damage or wear, such as loose connections or worn bearings.
- Overheating:Can be caused by excessive load, poor ventilation, or worn bearings.
- Noise and vibration:May indicate misalignment, unbalanced rotor, or worn bearings.
- Loss of power:Can be caused by electrical faults, open circuits, or worn brushes.
- Improving efficiency:Developing new materials and designs to reduce energy losses.
- Increasing power density:Designing motors that can deliver more power in a smaller size.
- Reducing noise and vibration:Implementing advanced noise suppression techniques.
- Wireless power transmission:Eliminating the need for physical connections to power motors.
- New applications:Exploring new applications for electric motors, such as in wearable devices and exoskeletons.
The power of an electric motor refers to its ability to perform work and is measured in watts or horsepower.
An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. It’s basically a machine that converts electricity into motion. Just like an electric motor is a device that converts electrical signals into physical movement, allowing devices to function.
This transformation process is what makes electric motors so useful in a wide range of applications, from powering household appliances to driving industrial machinery.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Electric Motors
Proper maintenance is crucial for the longevity and performance of electric motors. Regular maintenance includes:
Common troubleshooting issues for electric motors include:
Future Developments in Electric Motor Technology
Current research and trends in electric motor technology focus on:
Final Wrap-Up
As electric motor technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more transformative applications in the years to come. From powering self-driving cars to enabling the development of advanced robotics, electric motors are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping our future.
An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. For example, an electric heater is rated 1500w , which means it uses 1500 watts of electricity to generate heat. An electric motor, on the other hand, uses electricity to create motion.
Their efficiency, reliability, and versatility make them the driving force behind a wide range of innovations that will continue to improve our lives and redefine the boundaries of what’s possible.
An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. Similar to how an electric heater is rated at a certain wattage, an electric motor is rated by its power output in watts or horsepower. An electric motor’s power output determines the amount of mechanical work it can perform.
Popular Questions
What is the basic principle behind the operation of an electric motor?
An electric motor operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an electric current flows through a conductor placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force. This force causes the conductor to move, and the resulting motion is converted into mechanical energy.
What are the different types of electric motors?
There are various types of electric motors, each with its own advantages and applications. Some common types include DC motors, AC motors, synchronous motors, and stepper motors.
What are the main components of an electric motor?
The main components of an electric motor typically include a stator, rotor, windings, and a power source. The stator and rotor are the stationary and rotating parts of the motor, respectively, while the windings are responsible for generating the magnetic field.
An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. For instance, an electric lamp glows due to the conversion of electrical energy into light energy an electric lamp glows due to . Similarly, an electric motor transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy, enabling the rotation of its shaft.
An electric motor is a device which transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. However, the concept of electrical energy transformation extends beyond motors. Take, for instance, an electric lamp of 100 ohm . It transforms electrical energy into light energy.
Similarly, an electric motor transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy.