An electric motor may give noise due to a variety of factors, ranging from mechanical issues to electrical faults. Understanding the causes of motor noise is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintaining optimal performance.
An electric motor may give noise due to various factors such as mechanical vibrations, magnetic fields, and air movement. Similarly, an electric lamp glows due to the flow of electricity through a filament, which causes it to heat up and emit light.
Returning to the topic of electric motors, the noise produced can be minimized by using noise-absorbing materials, optimizing the motor’s design, and ensuring proper lubrication.
This comprehensive guide explores the different causes of electric motor noise, including mechanical issues, electrical faults, bearing problems, environmental factors, and design considerations. By delving into these aspects, we aim to provide a thorough understanding of the causes of motor noise and equip you with the knowledge to identify and address these issues effectively.
An electric motor may give noise due to various factors, such as electromagnetic interference, mechanical vibrations, or bearing wear. While it’s a common issue, it’s not the only one that can affect electrical appliances. For instance, an electric heater raises the temperature of 120g of water by converting electrical energy into heat, which can lead to thermal expansion and noise.
Similarly, an electric motor may give noise due to thermal expansion or contraction of its components, especially if they are made of different materials with different thermal expansion coefficients.
Electric Motor Noise: Causes and Mitigation: An Electric Motor May Give Noise Due To
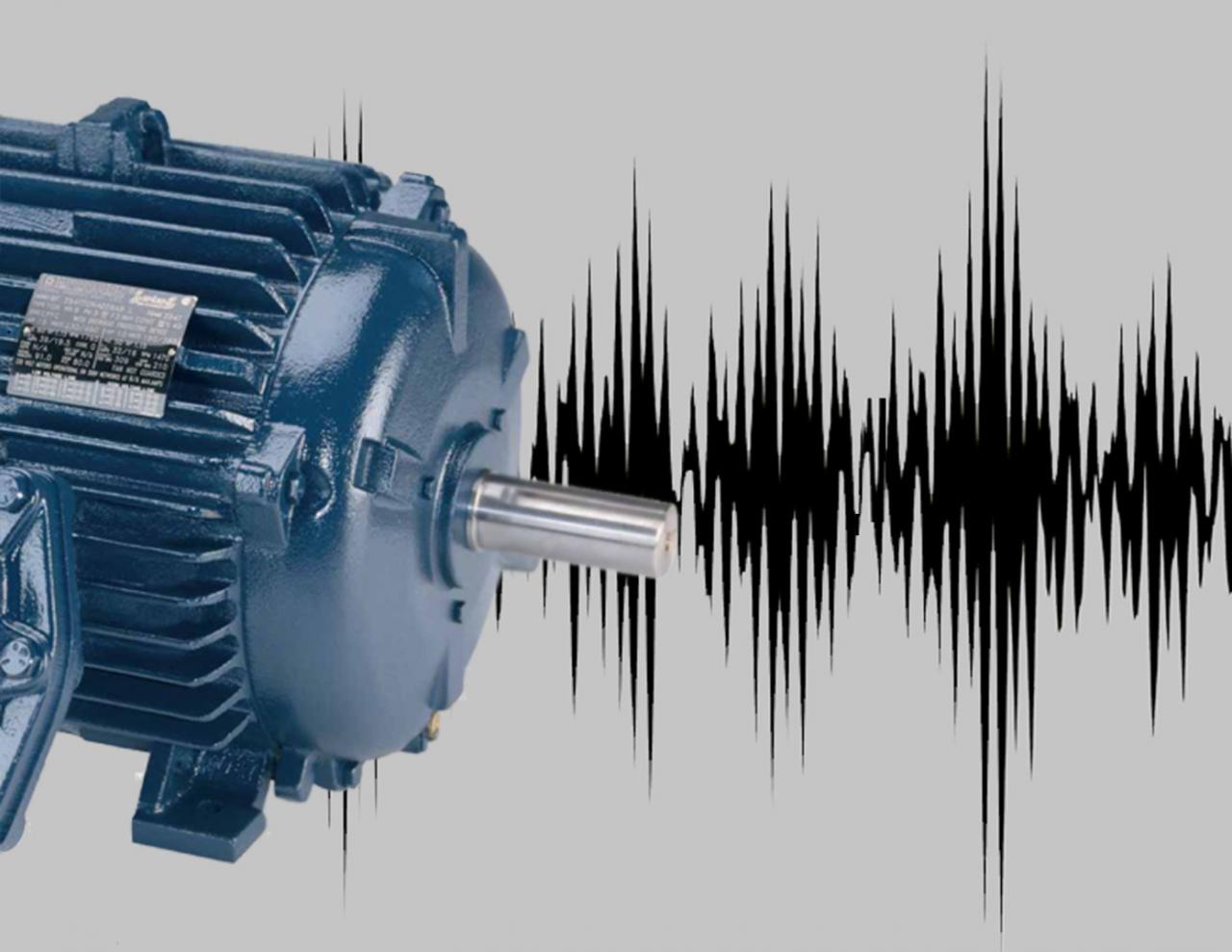
Electric motors are essential components in various industrial and domestic applications. However, they can generate noise during operation, which can be a nuisance or even a safety hazard. Understanding the causes of motor noise is crucial for effective mitigation and maintenance.
An electric motor may give noise due to a number of factors, including the type of motor, the speed at which it is running, and the load it is under. One common cause of noise in electric motors is the interaction between the stator and the rotor.
The stator is the stationary part of the motor, while the rotor is the part that rotates. When the rotor is spinning, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field of the stator. This interaction can create noise, especially if the motor is running at a high speed.
For example, an electric kettle consumes 1kw of power and it has an electric motor inside that may give noise due to the interaction between the stator and the rotor.
Mechanical Issues
Mechanical issues can contribute significantly to electric motor noise. These include:
- Bearing wear:Worn bearings can cause excessive vibration and noise.
- Rotor imbalance:An unbalanced rotor can create vibration and noise due to uneven weight distribution.
- Misalignment:Misaligned motor components can lead to excessive friction and noise.
- Loose fasteners:Loose bolts or screws can vibrate and generate noise.
Electrical Faults
Electrical faults can also cause electric motor noise. These include:
- Short circuits:Short circuits can cause arcing and sparking, leading to noise.
- Insulation breakdown:Insulation breakdown can result in current leakage and noise.
- Ground faults:Ground faults can create a path for current to flow through the motor frame, causing noise.
Bearing Problems
Bearings play a crucial role in supporting the motor shaft and reducing friction. However, bearing issues can contribute to noise:
- Wear:Worn bearings can cause increased vibration and noise.
- Misalignment:Misaligned bearings can lead to uneven loading and noise.
- Lubrication problems:Insufficient or improper lubrication can cause bearing wear and noise.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also affect electric motor noise:
- Temperature:Extreme temperatures can affect bearing lubrication and motor operation, leading to noise.
- Humidity:High humidity can cause corrosion and insulation breakdown, resulting in noise.
- Dust:Dust and debris can accumulate on motor components, causing friction and noise.
Design Considerations, An electric motor may give noise due to
Motor design factors can influence noise levels:
- Size:Larger motors tend to generate more noise than smaller motors.
- Speed:High-speed motors typically produce more noise than low-speed motors.
- Winding configuration:Different winding configurations can affect motor noise levels.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the noise produced by an electric motor can be attributed to a multitude of factors, each requiring specific attention for effective resolution. By understanding the underlying causes of motor noise, technicians and engineers can diagnose and rectify these issues promptly, ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of electric motors in various applications.
The noise that an electric motor makes can be due to a variety of factors, including the type of motor, the load it is under, and the environment in which it is operating. One common cause of noise in electric motors is electromagnetic interference (EMI).
EMI can occur when the motor’s magnetic field interacts with other electrical devices, such as an electric lamp of 100 ohm . EMI can cause the motor to produce a humming or buzzing sound.
FAQs
What are the most common mechanical issues that can cause electric motor noise?
Misalignment, bearing wear, and rotor imbalance are among the most prevalent mechanical issues that contribute to electric motor noise.
Can electrical faults lead to noise generation in electric motors?
An electric motor may give noise due to electromagnetic forces. Like the humming noise from an electric kitchen utensil due to electromagnetic forces acting on the coil windings and the stator core. The noise can also be caused by mechanical vibrations, such as those caused by the imbalance of the rotor or by the bearings.
These vibrations can be transmitted to the housing of the motor and radiated as noise.
Yes, electrical faults such as short circuits, insulation breakdowns, and loose connections can cause excessive noise in electric motors.
How do bearing problems affect the noise levels of electric motors?
Bearing issues, including wear, misalignment, and lubrication problems, can increase friction and vibration, resulting in elevated noise levels.
What environmental factors can influence electric motor noise?
Temperature, humidity, and dust can impact the noise produced by electric motors, affecting their cooling and lubrication capabilities.
How can design considerations contribute to noise generation in electric motors?
Motor size, speed, and winding configuration are among the design factors that can influence the noise levels of electric motors.
An electric motor may give noise due to mechanical vibration, magnetic noise, or aerodynamic noise. As an electric motor runs, it can cause vibrations in the surrounding air, which can be heard as noise. An electric heater with the total surface area of 0.25 can also produce noise, but the noise is usually at a lower frequency and is not as noticeable.
The noise from an electric motor can be reduced by using vibration isolation mounts, soundproofing materials, or by changing the design of the motor.
Yo, check it, an electric motor might be making all that racket because of some internal beef. But hold up, let’s not forget that an electric motor is a device that converts electricity into mechanical energy. So, when that juice flows through the motor, it can create a magnetic field that makes the motor spin.
But if there’s some friction or other issues, that spinning can lead to some annoying noise.
An electric motor may give noise due to vibrations or electromagnetic interference. Speaking of amperes, did you know that an electric motor draws 150 amperes ? That’s a lot of juice! Back to noise, an electric motor may also give noise due to mechanical problems such as bearing wear or misalignment.
An electric motor can give off noise due to vibrations or electromagnetic interference. An electric motor converts electrical energy into energy through the interaction of magnetic fields, and this process can sometimes create audible sounds. The noise level of an electric motor can vary depending on its design, size, and operating conditions.