An electric field of – In the realm of physics, electric fields reign supreme, shaping the interactions between charged particles and influencing the behavior of matter. From the spark of lightning to the hum of an electric motor, electric fields play a pivotal role in our world.
An electric field of acoustic guitars is gaining popularity due to their ability to play like electric guitars. Acoustic guitars that play like electric guitars are a hybrid of acoustic and electric guitars, offering the best of both worlds. The electric field of acoustic guitars is created by a pickup that converts the vibrations of the strings into an electrical signal.
This signal is then amplified and sent to a speaker, producing a sound that is similar to an electric guitar. However, the acoustic guitar still retains its natural acoustic sound, making it a versatile instrument that can be used in a variety of genres.
This guide delves into the captivating realm of electric fields, unraveling their properties, sources, effects, and practical applications.
As we embark on this electrifying journey, we will explore the strength and direction of electric fields, uncover the relationship between electric fields and electric potential, and discover how charges and electric dipoles generate these invisible forces. We will witness the effects of electric fields on charged particles, tracing their motion and observing their response to these invisible forces.
An Electric Field
An electric field is a region of space around a charged object where other charged objects experience a force. The electric field is created by the electric charge of the object, and its strength and direction depend on the magnitude and sign of the charge.
Electric fields are invisible, but their effects can be observed by the way they affect charged objects. For example, a charged object will experience a force when it is placed in an electric field. The force will be either attractive or repulsive, depending on the sign of the charge and the direction of the electric field.
Properties of an Electric Field, An electric field of
The strength of an electric field is measured in volts per meter (V/m). The direction of an electric field is indicated by the direction of the force that it would exert on a positive charge.
An electric field of 1000 volts per meter can cause a material to hold an electrical charge. This ability to hold an electrical charge is called capacitance. Capacitance is measured in farads. The larger the capacitance, the more charge a material can hold.
An electric field of 1000 volts per meter can cause a material with a capacitance of 1 farad to hold a charge of 1 coulomb.
The electric field around a point charge is spherically symmetric, meaning that it has the same strength and direction in all directions from the charge.
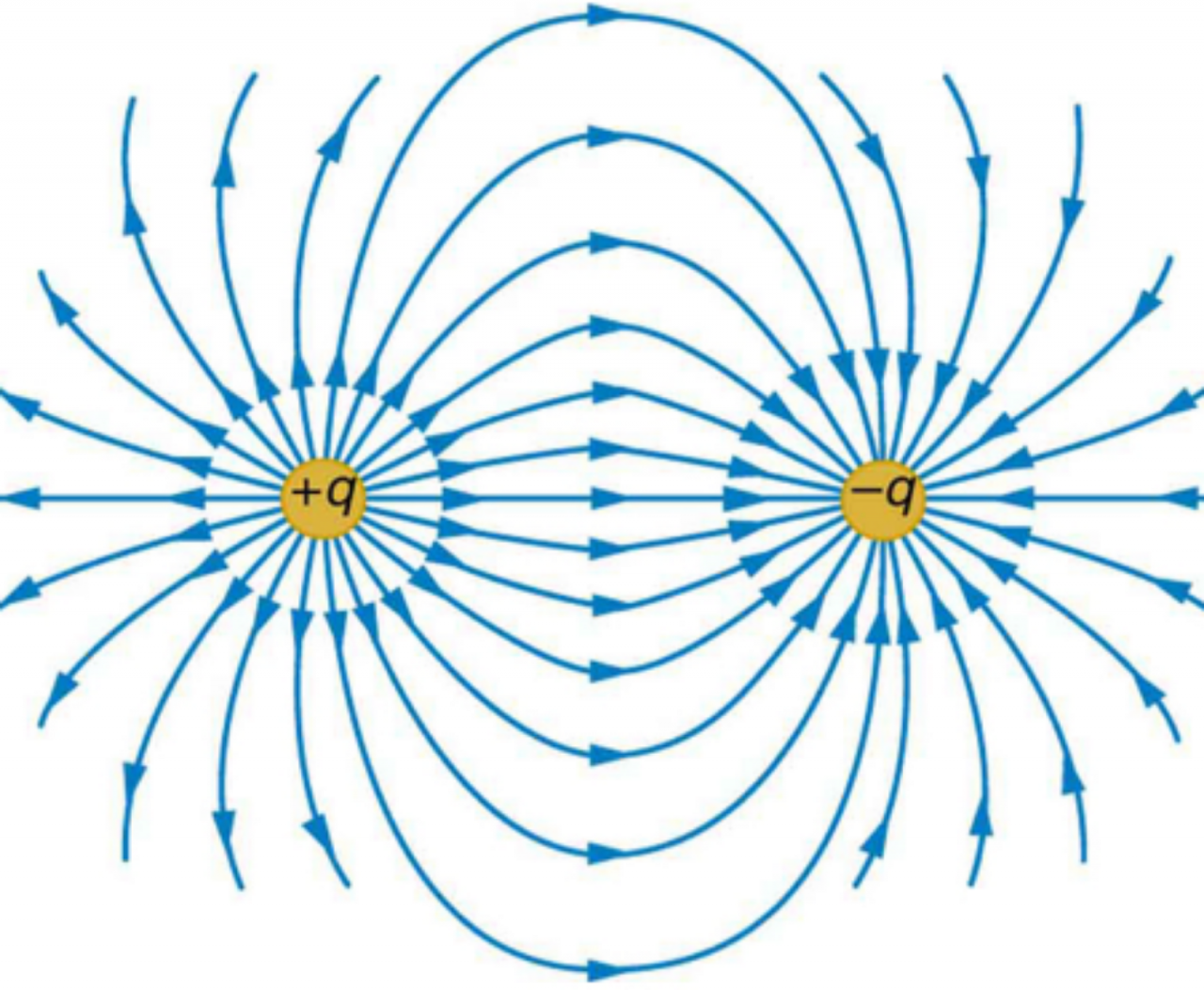
An electric field of a non-uniform nature can be caused by a wide variety of things, one of which is an electric dipole with dipole moment p . This field has many unique characteristics and can be measured using an electric field meter.
The electric field around a dipole is not spherically symmetric. The electric field is strongest near the ends of the dipole, and it is weakest in the middle.
If an electric field of 200 V/m exists around a long wire, the potential difference between two points 10 cm apart parallel to the wire is 20 V. This potential difference can be used to add a light switch to an electrical outlet , allowing you to control the flow of electricity to a light fixture.
Sources of Electric Fields
Electric fields are created by electric charges. A positive charge creates an electric field that points away from the charge, while a negative charge creates an electric field that points towards the charge.
Electric fields can also be created by electric dipoles. An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite charges that are separated by a small distance.
Effects of Electric Fields
Electric fields can exert a force on charged objects. The force on a charged object is proportional to the strength of the electric field and the magnitude of the charge.
The force on a charged object can be either attractive or repulsive, depending on the sign of the charge and the direction of the electric field.
An electric field of electrons flowing in a conductor is a fundamental concept in electricity. When you need to extend the reach of your electrical system, adding an electrical outlet to an existing line is a common solution. However, it’s crucial to remember that this involves manipulating the electric field and should be done with caution to avoid electrical hazards.
Applications of Electric Fields
Electric fields are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Capacitors
- Electric motors
- Electrostatic precipitators
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, electric fields are a fundamental aspect of our physical world, shaping interactions between charged particles and influencing a wide range of phenomena. Their applications extend from the mundane to the extraordinary, from the humble capacitor to the awe-inspiring electric motor.
As we continue to explore the intricacies of electric fields, we unlock new possibilities and gain a deeper understanding of the universe that surrounds us.
An electric field of any kind is something to be respected. It can cause serious injury or death if not handled properly. That’s why it’s important to learn how to work with electricity safely before attempting any electrical work. One common task that homeowners may need to do is add an electrical outlet from a switch.
This can be a relatively simple task, but it’s important to follow the proper steps to ensure that it’s done safely. Adding an electrical outlet from a switch is a relatively simple task, but it’s important to follow the proper steps to ensure that it’s done safely.
Always remember to turn off the power at the breaker box before working on any electrical wiring.
FAQ: An Electric Field Of
What is an electric field?
An electric field is an invisible region of space surrounding an electric charge, where other charged particles experience a force due to the presence of the charge.
What are the properties of an electric field?
An electric field of, also known as an electrostatic field, exerts force on charged particles. This force alters the amount of voltage traveling through an electrical circuit, alters the amount of voltage traveling through an electrical circuit . By modifying the electric field of, the voltage and current within the circuit can be regulated.
Electric fields have both strength and direction, and they can be represented by electric field lines. The strength of an electric field is measured in volts per meter (V/m), and the direction indicates the force that would be exerted on a positive charge placed in the field.
What are the sources of electric fields?
Electric fields are created by electric charges. Positive charges create electric fields that point away from the charge, while negative charges create electric fields that point towards the charge.
What are the effects of electric fields?
Electric fields exert forces on charged particles. These forces can cause charged particles to accelerate, move in circles, or even be deflected.
What are some applications of electric fields?
Electric fields are used in a wide variety of applications, including capacitors, electric motors, and particle accelerators.