A charged particle in an electric field – Step into the electric arena where charged particles take center stage! Picture tiny particles, imbued with an electric charge, swirling within the invisible grip of an electric field. Like celestial dancers, they pirouette and leap, their every move dictated by the interplay of these electric forces.
Yo, check this out! When a charged particle gets into an electric field, it’s like a rockstar on stage. It starts groovin’ to the rhythm of the field, moving around like it’s got a party line to the power source.
And just like a band needs a clear path to make the music flow, the charged particle needs a smooth electrical path to keep its dance party going strong in the electric field.
In this electrifying exploration, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of charged particles in electric fields, unraveling the secrets of their motion, applications, and the experimental techniques that illuminate their behavior.
A charged particle in an electric field experiences a force that causes it to accelerate. This force can be used to do work, such as powering an electric motor. One example of producing electricity using a battery is a battery . A battery uses chemical reactions to create an electric field, which can then be used to power devices.
The force on a charged particle in an electric field is proportional to the strength of the field and the charge of the particle.
Charged Particles in Electric Fields: A Charged Particle In An Electric Field
Charged particles are particles that have an electric charge, either positive or negative. When placed in an electric field, these particles experience a force that can cause them to accelerate. Electric fields are regions of space around charged objects where other charged objects experience a force.
Examples of charged particles include electrons, protons, and ions, while examples of electric fields include those created by batteries, power lines, and lightning.
Much like a charged particle experiencing an electric field, the 20 lb turkey in an electric roaster is subject to the forces of electromagnetism. Read more about the 20 lb turkey in an electric roaster to gain insights into the behavior of charged particles in an electric field.
The turkey, when placed in the roaster, experiences a force due to the electric field, causing it to heat up and cook evenly.
Forces on a Charged Particle
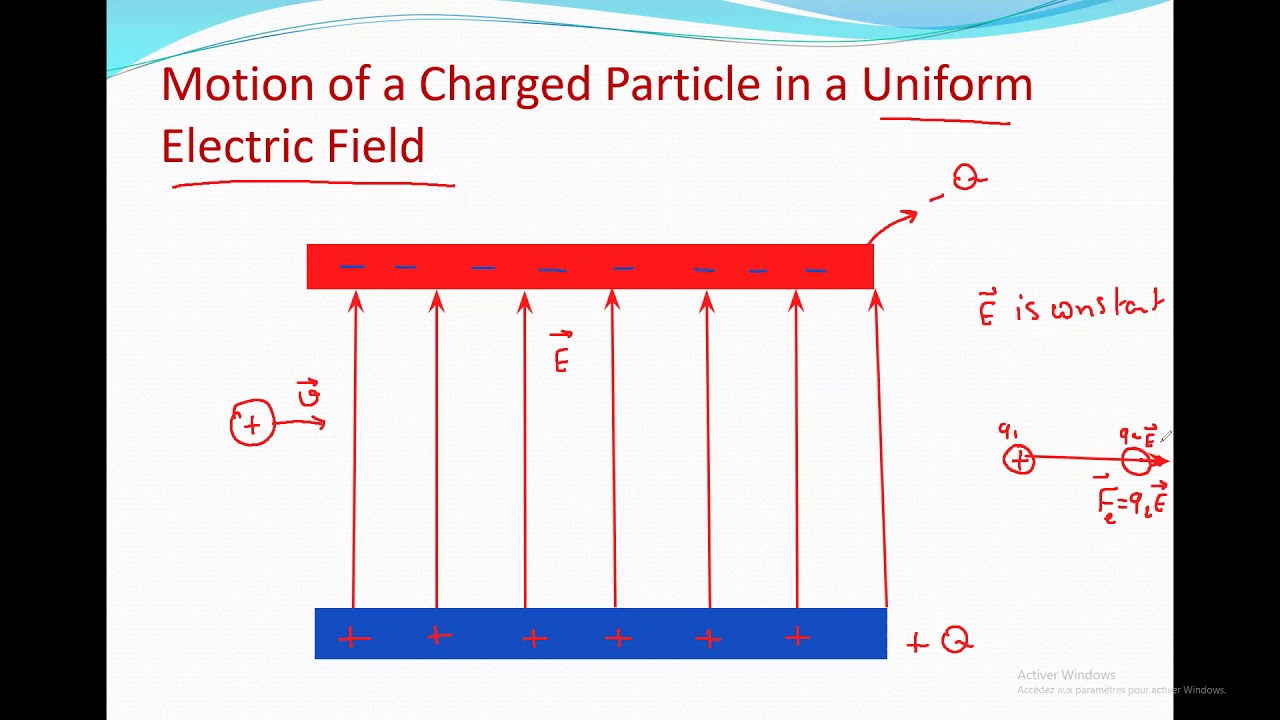
The electric force acting on a charged particle in an electric field is given by the equation F = qE, where F is the force, q is the charge of the particle, and E is the electric field strength. The direction of the force is determined by the sign of the charge: positive charges experience a force in the direction of the electric field, while negative charges experience a force in the opposite direction.
A charged particle in an electric field experiences a force that causes it to accelerate. This acceleration can be used to create an electric current, which is the flow of charged particles. Electric currents can be used to power devices such as a and an electric tampa . An electric current can also be used to create a magnetic field, which can be used to attract or repel other charged particles.
A charged particle in an electric field can also experience a torque, which is a force that causes it to rotate. This torque can be used to create an electric motor, which is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Motion of a Charged Particle
When a charged particle is placed in an electric field, it will experience a force and begin to accelerate. The trajectory of the particle will depend on the strength and direction of the electric field, as well as the charge and mass of the particle.
A charged particle in an electric field will experience a force due to the interaction between its charge and the electric field. This force can cause the particle to accelerate and move in a particular direction. In a similar vein, 50 years ago that wasn’t an electric fence , today it’s a common sight in many places.
Returning to our topic, the magnitude and direction of the force on a charged particle in an electric field depend on the strength of the electric field and the charge of the particle.
In a uniform electric field, charged particles will move in a straight line with constant acceleration.
A charged particle in an electric field experiences a force due to the interaction between its charge and the electric field. This force can cause the particle to accelerate, resulting in a change in its velocity. There are various ways to charge an object with static electricity, including friction, contact, and induction.
3 ways to charge an object with static electricity provides a comprehensive overview of these methods. Understanding the behavior of charged particles in electric fields is crucial for comprehending various electrical phenomena.
Applications
Charged particles in electric fields have a wide range of applications, including:
- Particle accelerators: These devices use electric fields to accelerate charged particles to very high speeds. This is used in research to study the fundamental properties of matter and in medical applications such as radiation therapy.
- Electron microscopes: These devices use electric fields to focus a beam of electrons to create a magnified image of a sample. This is used in a variety of fields, including biology, chemistry, and materials science.
Experimental Techniques
There are a variety of experimental techniques that can be used to study the motion of charged particles in electric fields. These techniques include:
- Millikan oil drop experiment: This experiment was used by Robert Millikan to measure the charge of an electron. It involves suspending a small oil drop in an electric field and observing its motion.
- Thomson’s cathode ray experiment: This experiment was used by J.J. Thomson to discover the electron. It involves passing a beam of electrons through a magnetic field and observing its deflection.
Mathematical Analysis, A charged particle in an electric field
The motion of a charged particle in an electric field can be described by the following equations:
- F = qE: The electric force acting on a charged particle.
- a = F/m: The acceleration of a charged particle.
- v = u + at: The velocity of a charged particle.
- s = ut + 1/2 at^2: The displacement of a charged particle.
Outcome Summary
Our journey through the realm of charged particles in electric fields has revealed the intricate dance they perform, guided by the invisible forces that govern their existence. From particle accelerators to electron microscopes, these charged particles have become indispensable tools, shaping our understanding of the world around us.
When a charged particle is placed in an electric field, it experiences a force that causes it to accelerate. This force is proportional to the charge of the particle and the strength of the electric field. The direction of the force is determined by the sign of the charge.
A positive charge will experience a force in the direction of the electric field, while a negative charge will experience a force in the opposite direction. A 2 inch diameter pulley on an electric motor is used to change the direction of the force on a charged particle.
The pulley is placed in the electric field, and the charged particle is passed through the pulley. The pulley changes the direction of the force on the charged particle, causing it to move in a different direction.
As we bid farewell to this electrifying topic, let the knowledge we’ve gained serve as a spark, igniting further exploration into the captivating world of charged particles and their electric adventures.
FAQ Resource
What is an electric field?
An electric field is a region of space around an electric charge where other charges experience an electric force.
What is a charged particle?
A charged particle is a particle that carries an electric charge, either positive or negative.
How does an electric field affect a charged particle?
An electric field exerts an electric force on a charged particle, causing it to accelerate in the direction of the force.