An electric cell is a source of – In the realm of energy, electric cells reign supreme as the unsung heroes powering our daily lives. From the humble batteries in our smartphones to the mighty fuel cells propelling electric vehicles, these energy powerhouses deserve a closer look. Dive into the electrifying world of electric cells as we explore their inner workings, diverse types, and countless applications that shape our modern world.
An electric cell is a source of electrical energy that provides power to devices. This energy flows through a complete circuit, which is an uninterrupted electrical path for current flow . The cell provides the driving force to keep the current flowing, allowing devices to function properly.
An electric cell is an essential component in many electronic devices, providing a reliable source of power for various applications.
Electric cells, the unsung heroes of our technological age, harness various energy sources to generate electricity. Chemical reactions, the sun’s rays, and even mechanical motion can fuel these versatile power sources, providing us with the energy we rely on. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of electric cells, uncovering the secrets behind their ability to power our devices and transform industries.
1. Concept of an Electric Cell
An electric cell, also known as a voltaic cell or galvanic cell, is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It consists of two electrodes (anode and cathode) immersed in an electrolyte solution. The anode is the negative electrode, while the cathode is the positive electrode.
An electric cell is a source of power, and electric cars are becoming increasingly popular. But before you make the switch, be aware of the 10 hidden costs of owning an electric car here . These costs can add up quickly, so it’s important to factor them into your decision.
An electric cell is a source of clean energy, but it’s also important to consider the hidden costs before making the switch to an electric car.
2. Sources of Energy in an Electric Cell
Electric cells can be powered by various energy sources, including chemical, solar, and mechanical energy. In chemical cells, the chemical energy stored in the reactants is converted into electrical energy. In solar cells, the energy from sunlight is converted into electrical energy.
In mechanical cells, the energy from mechanical work is converted into electrical energy.
An electric cell is a source of energy, which can be used to power devices like flashlights and cell phones. Electrical engineers design, develop, and maintain electrical systems, so they need to understand how electric cells work. You can learn more about advantages and disadvantages of being an electrical engineer to see if it’s the right career for you.
Electric cells are an important part of our everyday lives, and electrical engineers play a vital role in ensuring that they work properly.
3. Types of Electric Cells
Primary Cells
Primary cells are designed to be used once and then discarded. They consist of a non-rechargeable anode and cathode. Examples include alkaline batteries and zinc-carbon batteries.
An electric cell is a source of energy that can power devices like your phone or laptop. Inside an electric cell, there are tiny particles called atoms. An atom that is electrically neutral contains the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons.
When an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes electrically charged. This process is what creates the flow of electricity in an electric cell.
Secondary Cells
Secondary cells, also known as rechargeable batteries, can be recharged and used multiple times. They consist of a rechargeable anode and cathode. Examples include lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries.
An electric cell is a source of power, like the ones that make your favorite toys come to life. But when it’s time to take a break, you need a way to stop the flow of energy. That’s where a device that interrupts and de-energize an electrical circuit comes in.
It’s like a superhero that swoops in and turns off the power, giving your electric cell a chance to rest and recharge for the next adventure.
Fuel Cells, An electric cell is a source of
Fuel cells generate electricity through a chemical reaction between a fuel (usually hydrogen) and an oxidant (usually oxygen). They produce electricity as long as the fuel and oxidant are supplied.
An electric cell, like the ones you find in your TV remote, is a source of electrical energy. If you’ve ever wondered what it’s like to work with electricity on a larger scale, check out a day as an electrical engineer . You’ll learn about the challenges and rewards of designing, installing, and maintaining electrical systems that power our world.
And who knows, maybe you’ll even be inspired to pursue a career in this exciting field. An electric cell is a source of energy that can power small devices like a remote control, or it can be used to power large systems like the electrical grid.
4. Electrochemical Reactions in Electric Cells
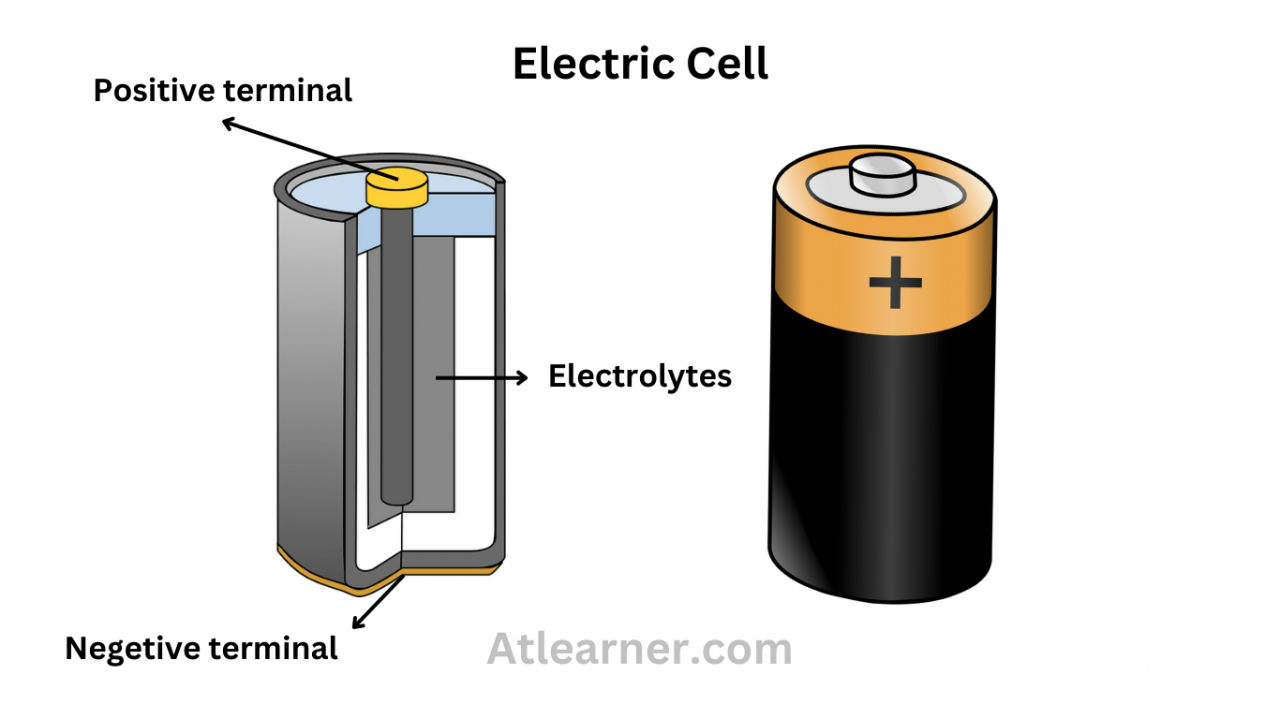
Electric cells rely on electrochemical reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons between the anode and cathode. Oxidation occurs at the anode, where electrons are released. Reduction occurs at the cathode, where electrons are accepted.
5. Factors Affecting Electric Cell Performance
Several factors can affect the performance of an electric cell, including temperature, concentration, and surface area. Higher temperatures generally increase cell voltage and current. Higher electrolyte concentrations also increase cell voltage and current. Larger surface areas of the electrodes increase the rate of electrochemical reactions.
6. Applications of Electric Cells
Electric cells have a wide range of applications, including:
- Batteries: Portable power sources for electronic devices, vehicles, and industrial equipment.
- Fuel cells: Power sources for vehicles, stationary power generation, and portable devices.
- Electroplating: Deposition of metal coatings on surfaces for decorative or functional purposes.
- Electrolysis: Separation of elements or compounds using electrical energy.
Last Point: An Electric Cell Is A Source Of
Electric cells, the silent workhorses of our energy landscape, have revolutionized the way we live. From powering our portable devices to propelling electric vehicles, these versatile energy sources continue to drive innovation and shape the future of energy. As we continue to explore and refine electric cell technology, we unlock even greater possibilities for sustainable and efficient energy solutions.
FAQ Overview
What is the basic principle behind an electric cell?
Electric cells generate electricity through electrochemical reactions, where chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
How do different types of electric cells differ?
Electric cells come in various types, such as primary (disposable), secondary (rechargeable), and fuel cells (continuous energy supply), each with unique characteristics and applications.
An electric cell is a source of electricity, and an all electric car is designed to run on that electricity. Electric cells are used in a variety of applications, from powering small devices like calculators to powering large electric vehicles like cars.
Electric cells are a clean and efficient way to power devices, and they are becoming increasingly popular as the world moves towards a more sustainable future.
What are the factors that affect the performance of an electric cell?
Temperature, concentration of reactants, and surface area of electrodes all play a role in determining the voltage, current, and power output of an electric cell.