An introduction to the circulatory system vocabulary – Step into the fascinating world of the circulatory system, the intricate network responsible for delivering life-sustaining oxygen and nutrients throughout your body. Join us as we embark on an exploration of its components, functions, and the vital role it plays in maintaining our well-being.
From the pumping heart to the tiniest capillaries, each part of the circulatory system works in harmony to ensure our survival. Let’s delve deeper into this remarkable system and uncover the secrets it holds.
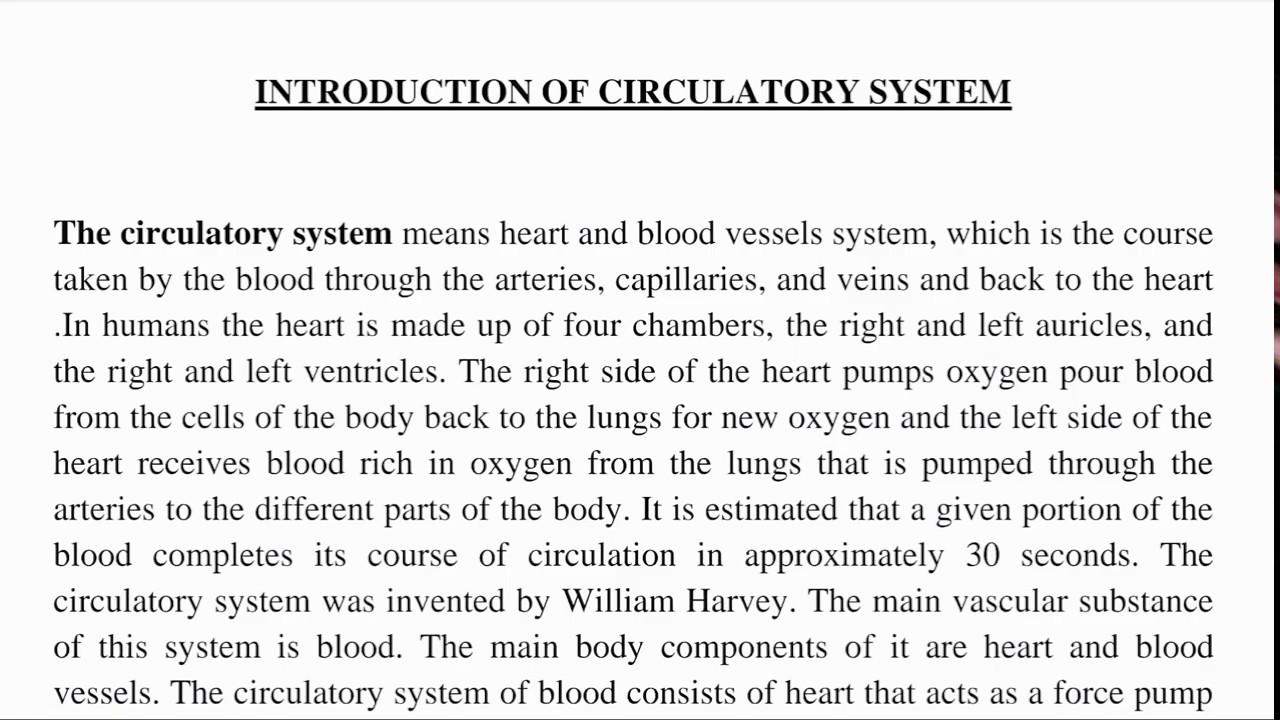
The circulatory system is a network of organs and vessels that transport blood throughout the body. It includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through the blood vessels, which carry it to the body’s tissues and organs.
The blood then returns to the heart through the veins. An i/o system call does not include the circulatory system, but it is essential for the body to function properly. The circulatory system provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, and it removes waste products.
It also helps to regulate body temperature and pH.
1. Introduction: An Introduction To The Circulatory System Vocabulary
The circulatory system is the network of organs and vessels that transport blood throughout the body, providing oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products.
When exploring the circulatory system, understanding the vocabulary is key. Dive into the intricacies of blood flow, heart valves, and vessels. Then, expand your knowledge horizons with an introduction to geographical information systems , delving into the world of spatial data and mapping technologies.
Returning to our circulatory journey, we’ll delve deeper into the anatomy and functions of this vital system.
It consists of the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), and blood.
2. Blood Vessels
Arteries
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body’s tissues.
They have thick, muscular walls that help propel blood forward.
Veins
Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Pumping through your veins, the circulatory system’s a maze of arteries, capillaries, and veins. To understand this human plumbing, we’ve got an intro to its vocab. But hey, while we’re on the topic of human biology, check out an international system for human cytogenetic nomenclature . It’s like a roadmap for the genetic code in our cells.
And back to our circulatory system, let’s dive deeper into the terms that make this blood-pumping machine tick.
They have thinner walls than arteries and contain valves to prevent blood from flowing backward.
Knowing the basics of the circulatory system vocabulary is like having a cheat sheet for understanding how your body works. Just like an examination of an organization’s accounting system helps you understand how a business operates, knowing the circulatory system vocabulary gives you insight into the flow of life within you.
From arteries to veins, each term plays a crucial role in maintaining the rhythm of your existence.
Capillaries
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels that allow for the exchange of oxygen and nutrients between the blood and the body’s tissues.
They have very thin walls and are permeable to allow for the passage of substances.
| Blood Vessel Type | Function | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Artery | Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart | Thick, muscular walls |
| Vein | Carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart | Thin walls, valves |
| Capillary | Exchange of oxygen and nutrients between blood and tissues | Very thin walls, permeable |
3. Heart
Structure
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest.
It has four chambers: two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers).
Function
The heart pumps blood throughout the body.
The atria receive blood from the body and pump it to the ventricles, which then pump it out to the body.
Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occur during one heartbeat.
It includes the filling of the heart with blood, the contraction of the heart to pump blood out, and the relaxation of the heart to allow it to fill again.
The circulatory system’s vocabulary is all about the heart, blood, and vessels that keep us alive. But when the immune system goes into overdrive, it can cause an exaggerated response . This can lead to inflammation, swelling, and pain. So, while we’re learning about the circulatory system’s vocabulary, let’s also keep an eye out for any signs of an exaggerated immune response.
Electrical Conduction System
The heart’s electrical conduction system coordinates the contraction of the heart.
It consists of the sinoatrial node (SA node), the atrioventricular node (AV node), and the bundle of His.
4. Blood
Composition
Blood is a complex fluid that consists of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Functions
Blood has many important functions, including:
- Transporting oxygen and nutrients to cells
- Removing waste products
- Regulating body temperature
- Fighting infection
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which carries oxygen.
Yo, get ready to pump up your circulatory system vocab! It’s like the highway system for your body, delivering blood and oxygen where it needs to go. And when it comes to keeping the bad guys out, you can count on an immune system cell that engulfs pathogens and other materials – like a superhero vacuum cleaner! So, let’s dive into the terms that’ll make you a circulatory system pro.
They are the most abundant type of blood cell.
White Blood Cells
White blood cells fight infection.
There are several different types of white blood cells, each with a specific function.
To delve into the captivating world of the circulatory system, let’s start with the basics – its vocabulary. Each term, like a beat in a heart’s rhythm, plays a vital role in understanding this intricate system. But hold on a sec! An information system always serves as a valuable companion in our quest for knowledge, just like an information system always . Now, back to our circulatory adventure, let’s decode the vocabulary that pumps life into this essential system.
Platelets, An introduction to the circulatory system vocabulary
Platelets help to form blood clots.
Pumping blood is the circulatory system’s jam, but did you know that equilibrium systems are like the VIP section for chemical reactions? Check out an equilibrium system for the reaction between hydrogen and iodine to see how these systems keep things balanced.
And hey, don’t forget about those circulatory system vocab words, they’re the VIPs of the biology world.
They are essential for stopping bleeding.

5. Blood Pressure
Definition
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood on the walls of blood vessels.
It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
The circulatory system vocabulary includes terms like “artery” and “vein,” which describe the vessels that carry blood throughout the body. Understanding these terms is crucial, especially when discussing an inherited degenerative disease of the muscular system . Such diseases affect the muscles’ ability to function, impacting the circulatory system’s efficiency in delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body.
Importance
Blood pressure is important because it ensures that blood is delivered to all parts of the body.
High blood pressure can damage blood vessels and lead to serious health problems.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is affected by a number of factors, including:
- Age
- Weight
- Diet
- Exercise
- Stress
Measuring Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is measured using a sphygmomanometer.
The sphygmomanometer is placed around the upper arm and inflated until the blood flow is stopped.
The pressure is then released slowly and the blood pressure is recorded when the blood flow is first heard.
6. Cardiovascular Diseases
Common Cardiovascular Diseases
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmia
Causes
Cardiovascular diseases are caused by a number of factors, including:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
Symptoms
The symptoms of cardiovascular diseases vary depending on the type of disease.
Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Palpitations
Treatment Options
The treatment options for cardiovascular diseases vary depending on the type of disease.
Common treatments include:
- Medication
- Surgery
- Lifestyle changes
Prevention
There are a number of things you can do to prevent cardiovascular diseases, including:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Quitting smoking
- Managing stress
Closing Summary
As we conclude our journey into the circulatory system, we marvel at the incredible complexity and efficiency of this life-sustaining network. Its components, working in unison, create a symphony of life, delivering nourishment and removing waste with remarkable precision.
Understanding the circulatory system empowers us to appreciate the intricate workings of our bodies and to make informed choices that support its health. Let us embrace this knowledge and strive to keep our circulatory systems strong and vibrant for years to come.
Essential FAQs
What is the function of the circulatory system?
The circulatory system is responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other essential substances throughout the body while removing waste products.
What are the main components of the circulatory system?
The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), and blood.
How does blood pressure work?
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of blood vessels. It is influenced by factors such as heart rate, blood volume, and the elasticity of blood vessels.