An integral part of the autonomic nervous system – The autonomic nervous system (ANS), an integral part of our body’s machinery, operates like a silent guardian, orchestrating essential functions without conscious effort. From regulating our heartbeat to controlling digestion, the ANS plays a pivotal role in maintaining our overall well-being.
An integral part of the autonomic nervous system, the enteric nervous system controls the digestive system. Like an example of lotic system , the enteric nervous system operates independently of the central nervous system, regulating digestion, absorption, and elimination. It’s a complex network of nerves and neurons that allows the digestive system to function without conscious control.
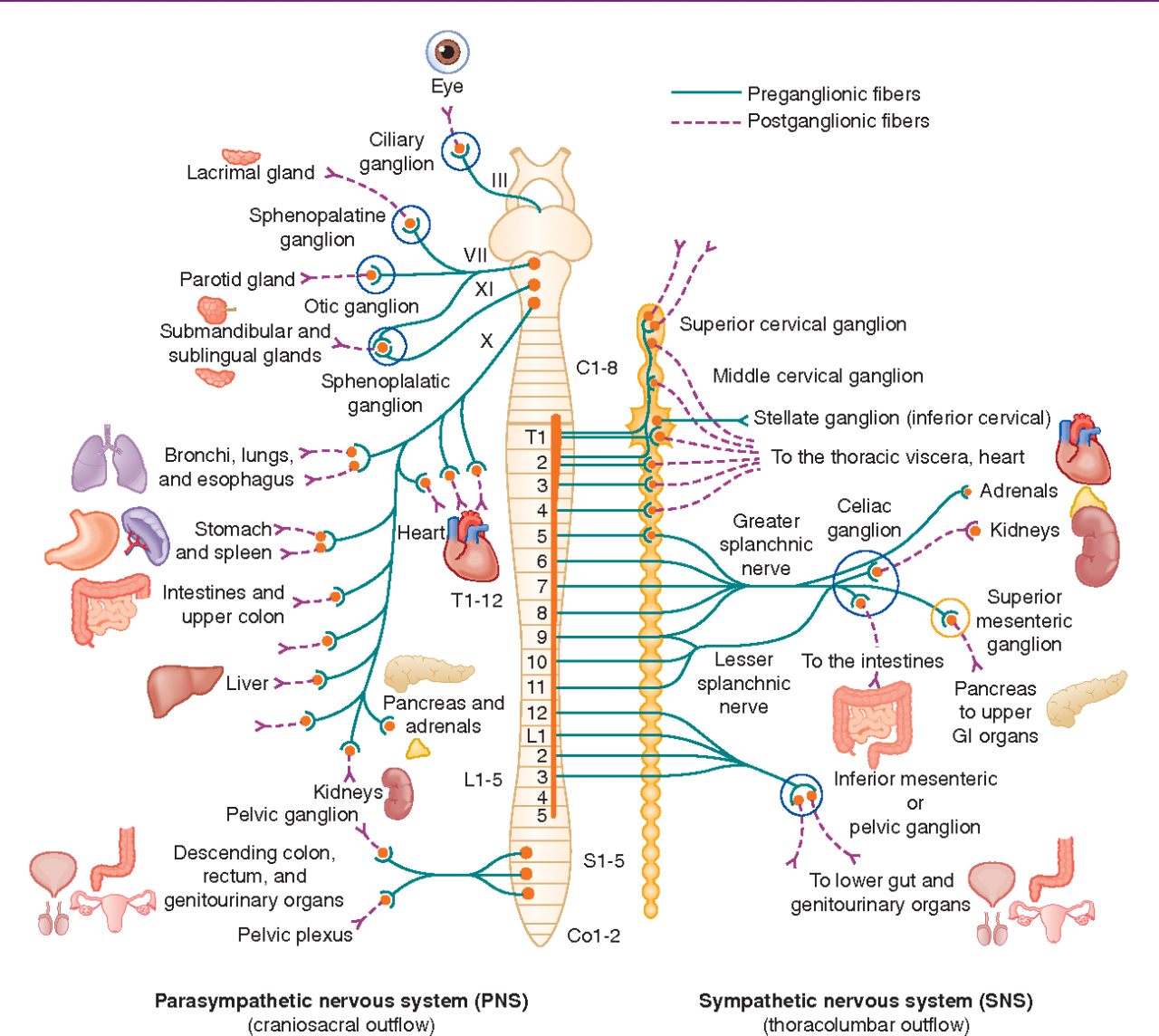
Composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions, the ANS acts as a delicate balancing act, ensuring the body’s homeostasis amidst ever-changing internal and external environments.
The vagus nerve, an integral part of the autonomic nervous system, is like a cosmic messenger, connecting our bodies to the celestial tapestry. Just as an icy small solar system body orbits its star, the vagus nerve dances through our bodies, sending signals that regulate everything from digestion to heart rate, connecting us to the symphony of life.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a division of the peripheral nervous system that innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. It is responsible for regulating bodily functions that are not consciously controlled, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and respiration.
An integral part of the autonomic nervous system, the sympathetic nervous system, responds to stressful situations and triggers a ‘fight or flight’ response. This is similar to the way an example of an open source operating system would respond to a user’s commands.
The sympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating bodily functions.
The ANS is divided into two main divisions: the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division.The sympathetic division is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. When the body is under stress, the sympathetic division releases hormones such as adrenaline and noradrenaline, which increase heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration.
The vagus nerve, an integral part of the autonomic nervous system, is responsible for regulating heart rate, digestion, and other bodily functions. However, an error occurred in the underlying security system can disrupt the vagus nerve’s function, leading to a variety of health problems.
Therefore, maintaining the integrity of the vagus nerve is crucial for overall well-being.
The parasympathetic division is responsible for the “rest and digest” response. When the body is at rest, the parasympathetic division releases hormones such as acetylcholine, which decrease heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration.
The vagus nerve, an integral part of the autonomic nervous system, plays a crucial role in regulating bodily functions. Scientists are developing innovative imaging techniques, like an improved imaging system that corrects ms2-induced rna destabilization , to better understand the vagus nerve’s intricate connections.
This breakthrough could pave the way for advancements in treatments targeting conditions linked to the autonomic nervous system, ultimately enhancing our comprehension of this vital component.
Components of the ANS
The ANS is composed of three main components: the brain, the spinal cord, and the ganglia. The brain and spinal cord are the central components of the ANS, and they receive and process information from the body. The ganglia are clusters of nerve cells that are located throughout the body.
They relay information between the brain and spinal cord and the organs and tissues that they innervate.
An integral part of the autonomic nervous system is the enteric nervous system, which controls the digestive system. This system is made up of neurons that are similar to those found in the brain and spinal cord. In fact, the enteric nervous system can function independently of the brain and spinal cord, which is why you can still digest food even if you’re unconscious.
An immune system cell called the plasma cell produces thousands antibodies that help fight off infection. The enteric nervous system works closely with the immune system to protect the digestive system from harmful bacteria and viruses.
Neurotransmitters of the ANS
The ANS uses a variety of neurotransmitters to communicate with its target organs and tissues. The most common neurotransmitters are acetylcholine and noradrenaline. Acetylcholine is released by the parasympathetic division, and it has a calming effect on the body. Noradrenaline is released by the sympathetic division, and it has a stimulating effect on the body.
The autonomic nervous system is an integral part of our body’s functions, controlling everything from heart rate to digestion. Just like an ERP system is an information system based on integrated modules, the autonomic nervous system works in a similar way, integrating various functions to maintain our overall well-being.
Regulation of Heart Rate
The ANS plays a key role in regulating heart rate. The sympathetic division increases heart rate, while the parasympathetic division decreases heart rate. The ANS also regulates the strength of the heart’s contractions.
Regulation of Blood Pressure
The ANS also plays a key role in regulating blood pressure. The sympathetic division increases blood pressure, while the parasympathetic division decreases blood pressure. The ANS also regulates the diameter of blood vessels.
The autonomic nervous system, an integral part of our bodies, operates without conscious control, just like the ideal education system that teaches students essential skills and knowledge effortlessly, nurturing their minds and shaping them into well-rounded individuals. This system, like the autonomic nervous system, becomes an inseparable part of their lives, empowering them to navigate the complexities of the world.
Regulation of Digestion
The ANS plays a key role in regulating digestion. The sympathetic division inhibits digestion, while the parasympathetic division stimulates digestion. The ANS also regulates the secretion of digestive juices.
Regulation of Respiration, An integral part of the autonomic nervous system
The ANS plays a key role in regulating respiration. The sympathetic division increases the rate and depth of respiration, while the parasympathetic division decreases the rate and depth of respiration. The ANS also regulates the diameter of the airways.
Clinical Significance
Dysfunction of the ANS can lead to a variety of health problems. For example, sympathetic overactivity can lead to high blood pressure, heart disease, and anxiety. Parasympathetic overactivity can lead to low blood pressure, bradycardia, and gastrointestinal problems.
Summary
In conclusion, the autonomic nervous system, like a symphony conductor, harmonizes a multitude of bodily functions, allowing us to navigate the complexities of life without giving conscious thought to every breath, heartbeat, or digestive process. Its intricate interplay with the body’s systems underscores its profound importance in our overall health and well-being.
The autonomic nervous system is an integral part of our bodies, controlling functions like heart rate and digestion. Just as an enterprise resource planning ERP system integrates various aspects of a business, the autonomic nervous system ensures seamless coordination within our bodies.
It’s like the conductor of an orchestra, orchestrating a harmonious symphony of physiological processes.
Top FAQs: An Integral Part Of The Autonomic Nervous System
What is the primary function of the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system’s primary function is to regulate involuntary bodily functions, ensuring homeostasis and adapting to changing internal and external environments.
How does the sympathetic division differ from the parasympathetic division?
The sympathetic division mobilizes the body’s resources for “fight or flight” responses, while the parasympathetic division promotes “rest and digest” activities, conserving energy and facilitating digestion.
Can dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system lead to health issues?
Yes, autonomic nervous system dysfunction can manifest in various health conditions, such as cardiovascular problems, digestive disorders, and chronic pain.