An electric dipole is defined as – Prepare to embark on an electrifying journey as we delve into the fascinating world of electric dipoles. These enigmatic entities, composed of two equal and opposite charges separated by a microscopic distance, hold the key to understanding a myriad of phenomena, from molecular polarity to the behavior of dielectric materials.
An electric dipole is defined as a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance. Dipoles are the building blocks of all matter, and they interact with each other to create electric fields and magnetic fields. An electric current produces a magnetic field , and the strength of the magnetic field is proportional to the strength of the current.
The direction of the magnetic field is determined by the direction of the current. An electric dipole is defined as a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance.
Join us as we unravel the properties, applications, and mathematical underpinnings of electric dipoles, shedding light on their profound impact on our technological advancements and everyday lives.
Electric Dipoles: The Basics
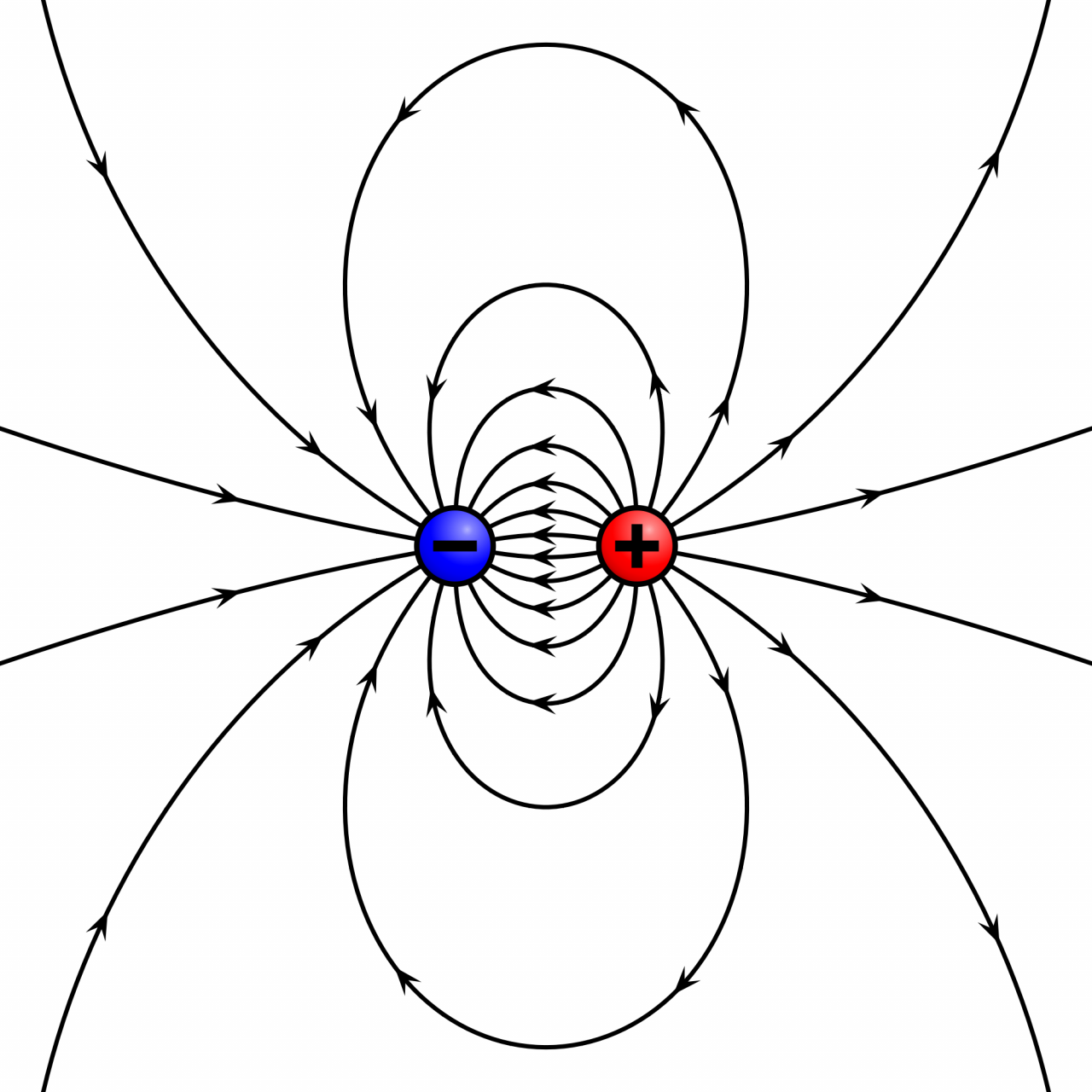
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance. Dipoles are found in nature and play a crucial role in various physical phenomena. Understanding electric dipoles is essential for comprehending electromagnetism and its applications.
An electric dipole is defined as a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance. This concept is used in many applications, including the design of electric bulbs. For example, an electric bulb is marked 60w , which means it consumes 60 watts of power.
This power is used to create an electric field between the two electrodes of the bulb, which causes the bulb to light up. The electric dipole is a fundamental concept in electricity and is used in many different applications.
Properties of Electric Dipoles
Electric dipoles create an electric field around them. The electric field strength and direction depend on the magnitude of the charges and the distance between them. The dipole moment, a vector quantity, characterizes the strength and orientation of the dipole.
An electric dipole is defined as a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance. Speaking of separation, have you heard about the age limit to ride an electric scooter ? It varies from state to state, so make sure to check before you hop on one.
Anyway, back to electric dipoles, they’re important in understanding many electrical phenomena, such as the behavior of dielectrics and the generation of electric fields.
Dipoles experience torque when placed in an external electric field, causing them to align with the field.
An electric dipole is defined as a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance. This is the basic building block of all electric circuits, and it’s what allows us to do things like turn on lights and charge our phones.
You can even add a switch to an electrical outlet adding a switch to an electrical outlet to control the flow of electricity. An electric dipole is defined as a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance, and it’s what makes all of this possible.
Applications of Electric Dipoles
Electric dipoles find applications in diverse fields. They help explain molecular polarity, which influences chemical bonding and intermolecular forces. Dipoles are crucial in understanding dielectric materials, which store electrical energy. Dipole antennas, used in communication systems, transmit and receive electromagnetic waves.
Mathematical Representation
The electric field of a dipole can be mathematically expressed using the following equation:
E = (1/4πε₀)
(p / r³),
An electric dipole is defined as two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance. An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. One way to add an electric motor to a bicycle is to mount it on the rear wheel.
Add an electric motor to a bicycle and you can enjoy the benefits of an electric bike without having to buy a new one. An electric dipole is defined as two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance.
where E is the electric field strength, ε₀ is the permittivity of free space, p is the dipole moment, and r is the distance from the dipole.
An electric dipole is defined as a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance. Back in the day, electric fences weren’t a thing . Instead, people used to keep their livestock in with barbed wire fences.
But today, electric dipoles are used in a variety of applications, from electric motors to lasers.
Comparison with Other Electric Configurations, An electric dipole is defined as
The electric field of a dipole differs from that of a point charge. A dipole’s field decreases more rapidly with distance than a point charge’s field. Dipoles are also distinct from quadrupoles, which have four charges instead of two. Dipole moments contribute to the overall electric field of a system, influencing the interactions between charged particles.
Last Recap: An Electric Dipole Is Defined As
Our exploration of electric dipoles has illuminated their pivotal role in shaping the electrical landscape of our world. From their ability to align molecules and influence dielectric properties to their practical applications in antennas and beyond, electric dipoles continue to captivate scientists and engineers alike.
As we bid farewell to this electrifying topic, let us carry forward the knowledge and insights we have gained, recognizing the profound impact that electric dipoles have on our understanding of the universe.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of the dipole moment?
The dipole moment quantifies the strength and orientation of an electric dipole, providing a measure of its ability to interact with electric fields.
How do electric dipoles contribute to the overall electric field of a system?
Electric dipoles can align themselves in the presence of an external electric field, creating a net electric field that differs from the field produced by individual charges.
What are some practical applications of electric dipoles?
An electric dipole is defined as a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance. This concept is essential in understanding electrical phenomena, from the behavior of electrons in atoms to the operation of electrical devices. For instance, if you’re looking to expand your home’s electrical capabilities, you may need to consider adding an additional electrical outlet . This involves creating a new electrical circuit and connecting it to your home’s electrical panel.
Understanding the principles of electric dipoles will help you grasp the fundamentals of electricity and make informed decisions about your home’s electrical system.
Electric dipoles find applications in dipole antennas, which are used for transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves, and in dielectric materials, which exhibit unique electrical properties due to the alignment of their molecular dipoles.