Add an efi system partition ubuntu – Prepare your Ubuntu system for the next level of boot performance with an EFI system partition. Discover its purpose, benefits, and seamless methods for integration, unlocking a faster and more reliable boot process.
By incorporating an EFI system partition, you’ll optimize your system’s boot sequence, ensuring a smoother and more efficient startup experience. Dive into this guide and witness the transformative power of an EFI system partition for your Ubuntu system.
Adding an EFI system partition to Ubuntu can be a daunting task, but it’s essential for those looking to run the latest operating systems. Just like understanding the basics of information systems ( 1 what is an information system ) is crucial for any tech enthusiast, setting up an EFI system partition is a necessary step for a seamless Ubuntu experience.
Introduction
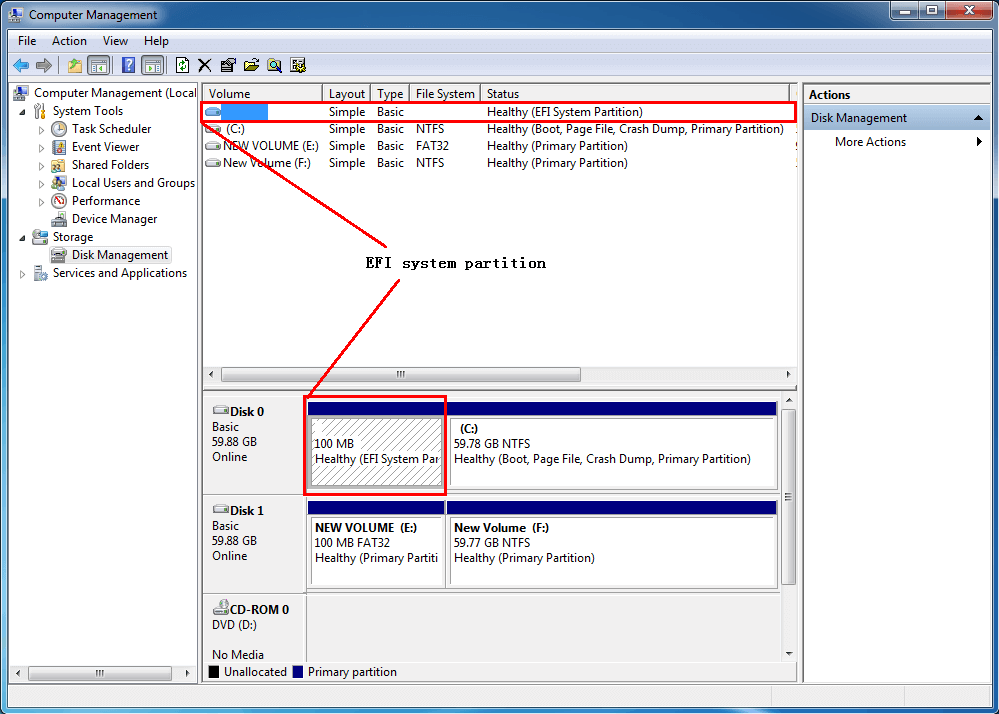
EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) system partitions are a crucial component of modern computers that use the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) firmware. They provide a way to store bootloaders and other essential files needed to boot the operating system. Adding an EFI system partition to a Ubuntu system offers several benefits, including improved boot times, enhanced security, and support for newer hardware.
In this article, we will explore the process of adding an EFI system partition to a Ubuntu system. We will cover the prerequisites, different methods for creating the partition, configuring the system to boot from it, and troubleshooting common issues.
Prerequisites
Before adding an EFI system partition to your Ubuntu system, ensure that your hardware and software meet the following requirements:
- A computer with a UEFI-compatible motherboard.
- A USB drive or DVD with the Ubuntu ISO image.
- A partition manager such as GParted or fdisk.
To check if your system meets these requirements, follow these steps:
- Restart your computer and enter the UEFI settings (usually by pressing F2 or Del during boot).
- Look for an option that mentions “UEFI” or “Secure Boot.” If you find this option, your motherboard supports UEFI.
- Download the Ubuntu ISO image and create a bootable USB drive or DVD.
- Boot from the USB drive or DVD and select “Try Ubuntu” without installing it.
- Once Ubuntu is loaded, open a terminal window and type the following command:
“`sudo parted
l
It’s a bummer when you’re trying to add an EFI system partition to Ubuntu and you hit a snag. But hey, don’t sweat it, even a large company like this one has its own inspection system to make sure everything runs smoothly.
So, take a deep breath, grab a cup of joe, and let’s get that EFI system partition added to Ubuntu.
When adding an EFI system partition to Ubuntu, it’s like creating a traditional economy, where resources are allocated based on custom and tradition. A traditional economy is an economic system is… just like how the EFI system partition manages boot information for Ubuntu, a traditional economy relies on established practices to distribute goods and services.
“`
This command will display a list of your system’s partitions. Look for a partition with the “EFI System” type.
Methods for Adding an EFI System Partition
There are two main methods for adding an EFI system partition to a Ubuntu system:
- Using the GParted graphical partition editor
- Using the fdisk command-line utility
Using GParted, Add an efi system partition ubuntu
GParted is a user-friendly graphical partition editor that makes it easy to create and manage partitions. To add an EFI system partition using GParted, follow these steps:
- Boot from the Ubuntu USB drive or DVD and select “Try Ubuntu” without installing it.
- Once Ubuntu is loaded, click on the “Activities” button and type “GParted.” Click on the GParted icon to launch the application.
- In the GParted window, select the disk where you want to create the EFI system partition. Right-click on the unallocated space and select “New.”
- In the “New Partition” window, set the following options:
- File system: FAT32
- Size: 512 MB (or larger)
- Label: EFI System Partition
- Click on the “Add” button to create the partition.
- Once the partition is created, click on the “Apply” button to save the changes.
Using fdisk
fdisk is a powerful command-line utility that can be used to create and manage partitions. To add an EFI system partition using fdisk, follow these steps:
- Boot from the Ubuntu USB drive or DVD and select “Try Ubuntu” without installing it.
- Once Ubuntu is loaded, open a terminal window and type the following command:
“`sudo fdisk
When it comes to partitioning your drive for Ubuntu, you’ll need to create an EFI system partition. This partition is used by the firmware to boot the system, and it’s essential for a successful installation. A system that has an infinite number of solutions is like an EFI system partition in that it provides a foundation for something greater.
Just as the EFI partition enables Ubuntu to boot, a system with infinite solutions allows for endless possibilities. So, when you’re partitioning your drive for Ubuntu, don’t forget to create an EFI system partition—it’s the key to unlocking the full potential of your system.
l
“`
This command will display a list of your system’s partitions.
- Identify the disk where you want to create the EFI system partition. It is usually the first disk listed, such as /dev/sda.
- Type the following command to enter fdisk mode:
“`sudo fdisk /dev/sda“`
A key step in configuring Ubuntu for UEFI systems is to create an EFI System Partition (ESP). ESPs are crucial for booting the operating system and storing firmware files. One of the advantages of using cloud-based ERP systems is an advantage of cloud-based erp systems.
is their ability to simplify data management and streamline operations. By leveraging cloud-based ERP systems, businesses can gain real-time visibility into their operations and make informed decisions to improve efficiency. As such, creating an ESP is an essential step for Ubuntu users to ensure a seamless and secure boot process.
- In fdisk mode, type the following commands:
“`gn
1
+512Mt
- 1
- 1
w“`
These commands will create a new partition of type 1 (EFI System Partition) with a size of 512 MB.
Configuring the EFI System Partition
Once you have created an EFI system partition, you need to configure it to boot Ubuntu. To do this, you need to update the GRUB bootloader configuration.
To update the GRUB bootloader configuration, follow these steps:
- Boot from the Ubuntu USB drive or DVD and select “Try Ubuntu” without installing it.
- Once Ubuntu is loaded, open a terminal window and type the following command:
“`sudo mount /dev/sda1 /mnt“`
This command will mount the EFI system partition to the /mnt directory.
- Copy the GRUB bootloader files to the EFI system partition:
“`sudo cp
r /boot/efi/EFI/ubuntu/ /mnt/EFI/
“`
- Update the GRUB bootloader configuration:
“`sudo grub-install
To add an EFI system partition in Ubuntu, you’ll need to create a new partition and format it as FAT32. You can use the GParted tool to do this. Once the partition is created, you can install the EFI bootloader on it.
A vendor managed inventory system refers to an inventory system where the vendor manages the inventory for the customer. This can help to reduce costs and improve efficiency. After installing the EFI bootloader, you can then boot from the new EFI system partition.
- -target=x86_64-efi
- -efi-directory=/mnt/EFI/ubuntu
- -bootloader-id=ubuntu
“`
- Reboot your computer and select Ubuntu from the boot menu.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter any problems while adding an EFI system partition, here are some common issues and their solutions:
- Error: “No EFI System Partition found.”
- Error: “Failed to boot from EFI System Partition.”
- Error: “Secure Boot is enabled.”
This error occurs if you have not created an EFI system partition. Follow the steps in the “Methods for Adding an EFI System Partition” section to create one.
This error occurs if the GRUB bootloader is not properly configured. Follow the steps in the “Configuring the EFI System Partition” section to update the GRUB bootloader configuration.
If you’re trying to add an EFI system partition to Ubuntu, you might be wondering if there’s a more modern approach. Well, just like a modern structure that uses an arch and dome system , there is! By utilizing the latest partitioning techniques, you can create an EFI system partition that’s both efficient and effective, making your Ubuntu installation more secure and reliable.
If your computer has Secure Boot enabled, you will need to disable it before you can boot from an EFI system partition. Consult your computer’s documentation for instructions on how to disable Secure Boot.
Advanced Topics
Once you have successfully added an EFI system partition to your Ubuntu system, you can explore some advanced topics, such as:
- Creating multiple EFI system partitions
- Using an EFI stub loader
You can create multiple EFI system partitions to store different bootloaders or kernels. This can be useful if you want to dual-boot multiple operating systems or if you want to experiment with different kernel versions.
An EFI stub loader is a small program that loads the main bootloader from the EFI system partition. This can be useful if you want to use a custom bootloader or if you want to troubleshoot boot problems.
Closing Notes: Add An Efi System Partition Ubuntu
With an EFI system partition seamlessly integrated into your Ubuntu system, you’ve achieved a new level of boot optimization. Experience faster boot times, improved stability, and the satisfaction of a well-tuned system. Embrace the benefits of an EFI system partition and elevate your Ubuntu experience to new heights.
Question Bank
What is an EFI system partition?
An EFI system partition is a small partition on your hard drive that stores boot-related files for your computer’s firmware.
Why should I add an EFI system partition to my Ubuntu system?
Adding an EFI system partition can improve your system’s boot time and stability, and it can also make it easier to troubleshoot boot problems.
How do I add an EFI system partition to my Ubuntu system?
You can add an EFI system partition to your Ubuntu system using the GParted graphical partition editor or the fdisk command-line utility.