In today’s digital realm, information systems reign supreme, orchestrating the seamless flow of data that empowers businesses and shapes our lives. Dive into the captivating world of 5 components of an information system, where hardware, software, data, procedures, and people converge to create a symphony of information mastery.
From the tangible realm of computers and servers to the intangible world of data and processes, each component plays a vital role in harnessing the power of information. Get ready to unravel the secrets of this digital ecosystem and discover how it shapes our interactions, drives innovation, and transforms the way we do business.
Information Systems: Five Essential Components
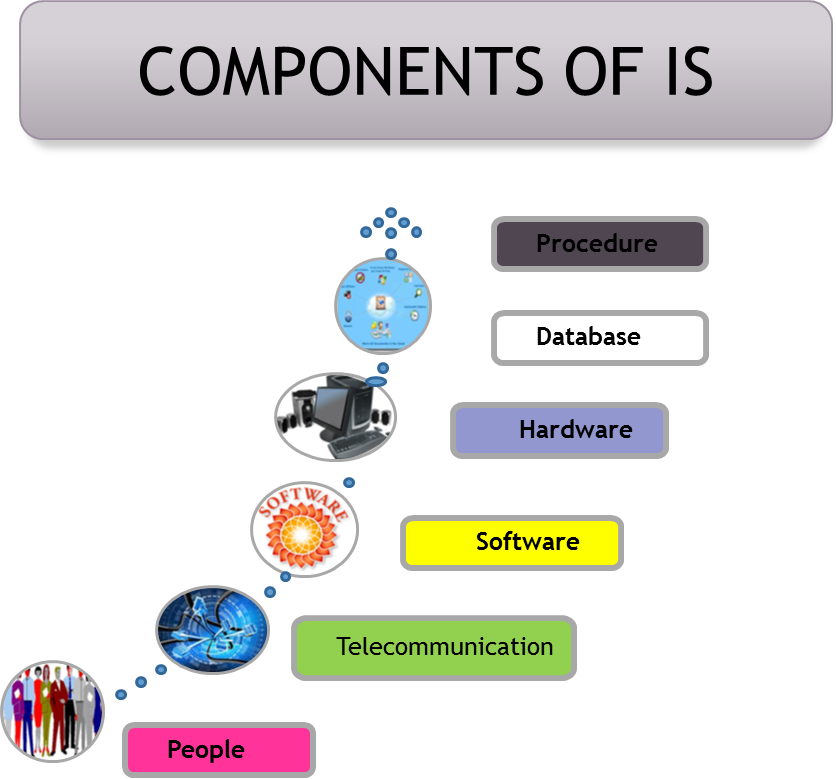
Information systems play a pivotal role in the modern world, enabling businesses and organizations to streamline operations, make informed decisions, and connect with customers. These systems are composed of five key components: hardware, software, data, procedures, and people.
1. Hardware
Hardware refers to the physical components of an information system. These components include computers, servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. Hardware provides the infrastructure for storing, processing, and transmitting data.
Examples of Hardware Devices
* Computers: Desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones
Servers
Physical or virtual machines that host and manage applications and data
Storage devices
Hard disk drives, solid-state drives, and cloud storage
Networking equipment
Routers, switches, and modems that connect devices to a network
Importance of Hardware Compatibility and Maintenance
Hardware components must be compatible with each other to ensure smooth operation. Regular maintenance is crucial to prevent hardware failures and extend the lifespan of the system.
2. Software
Software refers to the instructions and programs that run on hardware. It includes operating systems, application software, and utility programs. Software provides the functionality and user interface for an information system.
Types of Software
* System software:Manages the hardware and provides basic services, such as operating systems and network management software
Application software
Performs specific tasks, such as word processing, spreadsheets, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems
Importance of Software Updates and Security
Software updates fix bugs, improve performance, and add new features. Security updates are essential to protect against malware and cyberattacks.
3. Data
Data is the raw facts and figures that are processed and stored in an information system. Data can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
Types of Data
* Structured data:Data that is organized in a fixed format, such as tables in a database
Semi-structured data
Data that has some structure but is not as rigid as structured data, such as XML files
Unstructured data
Data that has no predefined structure, such as text documents and images
Importance of Data Management and Quality
Effective data management ensures that data is accurate, consistent, and accessible. Data quality is crucial for making informed decisions and avoiding errors.
4. Procedures
Procedures are the rules and guidelines that govern the operation of an information system. They describe how tasks are performed and who is responsible for each task.
Importance of Documenting and Following Procedures
Documented procedures provide clear instructions and ensure that tasks are performed consistently. Following procedures reduces errors and improves efficiency.
5. People
People are the users, operators, and managers of an information system. They provide the expertise and knowledge to operate the system effectively.
Importance of Training and User Support
Training ensures that users are proficient in using the system. User support provides assistance when users encounter problems or have questions.
Ethical and Social Implications of Information Systems, 5 components of an information system
Information systems can have ethical and social implications, such as privacy concerns, data breaches, and job displacement. It’s important to consider these implications when designing and using information systems.
Outcome Summary: 5 Components Of An Information System
As we reach the end of our exploration, it’s evident that 5 components of an information system are the cornerstone of our digital landscape. Hardware provides the physical foundation, software orchestrates the operations, data fuels the insights, procedures ensure efficiency, and people drive the innovation.
Together, they form a harmonious ecosystem that empowers us to navigate the complexities of the information age.
Remember, the effective utilization of these components is paramount for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital era. By embracing the power of information systems, we unlock endless possibilities for growth, efficiency, and innovation. The future of information is in our hands, and it’s brighter than ever before.
FAQ Summary
What is the primary function of hardware in an information system?
Hardware serves as the physical foundation, providing the computing power and storage capacity to process and store data.
How does software differ from hardware?
Software comprises the instructions and programs that direct the hardware, enabling it to perform specific tasks and manage data.
Why is data quality crucial in information systems?
Data quality is paramount as it directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of insights derived from the system.